Figure 6.
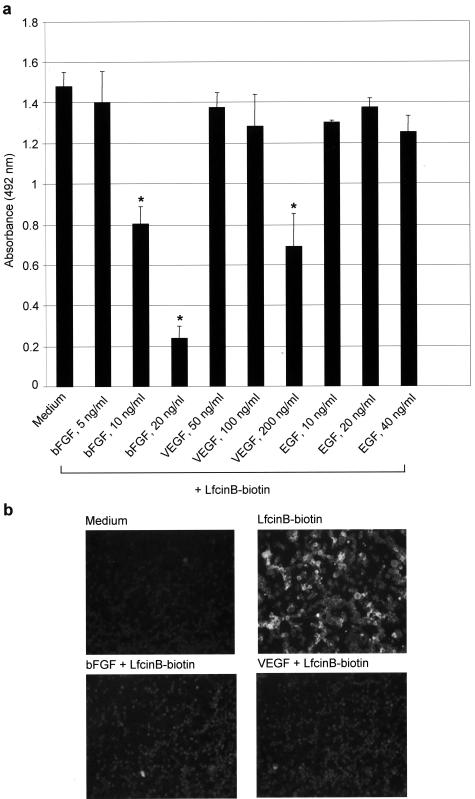
bFGF and VEGF165 inhibit LfcinB binding to HUVECs. a: Colorimetric analysis of the effect of growth factors on LfcinB-HUVEC interactions. HUVEC monolayers were exposed to biotinylated LfcinB (50 μg/ml) in the absence or presence of the indicated concentrations of bFGF, VEGF165, or nonheparin-binding EGF for 2 hours. HUVEC monolayers were then washed and incubated for 2 hours with streptavidin-HRP. After additional washes, 1,2-phenylenediamine substrate was added and absorbance was measured at 492 nm. Data are shown as mean absorbance ± SD of quadruplicate determinations. Background absorbance was 0.043 ± 0.001. Statistical significance relative to the LfcinB control was determined by the Tukey-Kramer multiple comparisons test; *P < 0.001. b: Determination by fluorescent microscopy of the effect of bFGF or VEGF165 on LfcinB-HUVEC interactions. HUVEC monolayers were exposed to medium alone or to biotinylated LfcinB (50 μg/ml) in the absence or presence of bFGF (20 ng/ml) or VEGF165 (200 ng/ml) for 2 hours. HUVEC monolayers were then washed and incubated with streptavidin-Texas Red. After additional washes, LfcinB binding to HUVECs was visualized by fluorescent microscopy. Original magnifications, ×200.