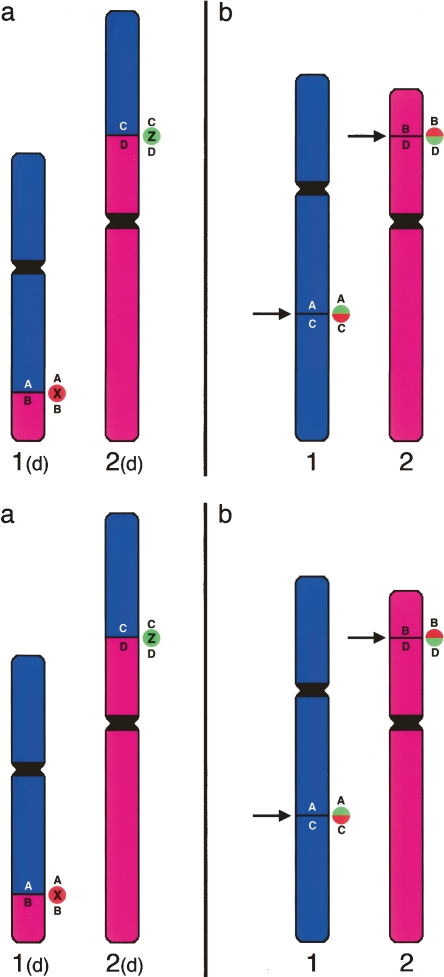
Figure 1.
Methodology to detect breakpoints by FISH. (a) Hypothetical gibbon chromosomes 1(d) and 2(d) are the derivatives of a translocation. The original human chromosomes are reported in b. The arrows indicate the breakpoints. Gibbon clones X or Z, spanning the breakpoints of chromosomes 1(d) and 2(d), respectively, contain a portion of both chromosomes 1 and 2. Both clones X and Z generate a “split signal” on the original human chromosomes. If cohybridized in different colors (red and green in the example), they will produce two distinct red and green signals on gibbon, but will produce split signals in humans that, because of proximity, will appear yellow (see Fig. 2).