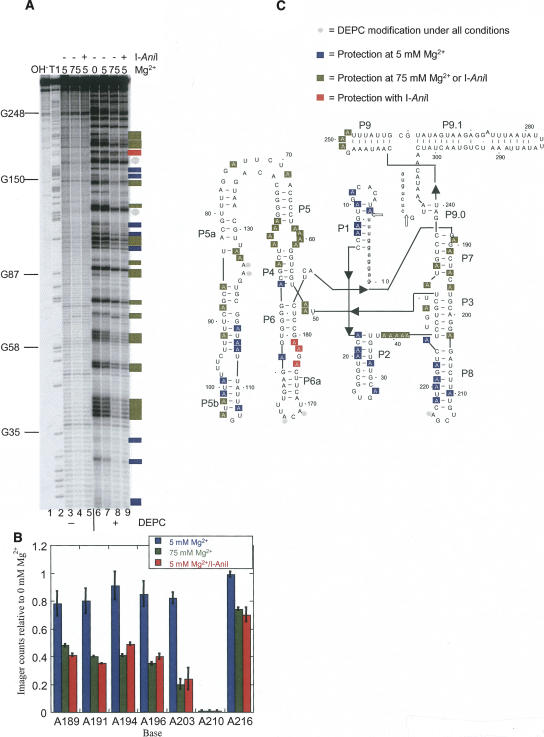
FIGURE 1.
Chemical structure mapping of the A.n. COB pre-RNA. (A) DEPC modification of end-labeled RNA. End-labeled A.n. COB was treated with DEPC in various concentrations of Mg2+ as well as in the presence of I-AniI. Sites of modification were cleaved by treatment with aniline and the products separated by denaturing gel electrophoresis. Lane 1, hydrolysis ladder; lane 2, G sequencing by partial T1 digestion; lanes 3–5, mock-treated RNA; lanes 6–9, DEPC-treated RNAs; lane 6, 0 mM Mg2+, lanes 3 and 7, 5 mM Mg2+; lanes 4 and 8, 75 mM Mg2+; lanes 5 and 9, 5 mM Mg2+ plus I-AniI. (B) Quantification of the DEPC mapping data encompassing the P7–P8 region. PhosophorImager counts in each lane were normalized and expressed as a ratio relative to 0 mM Mg2+. The histogram shows averaged ratios with the error bars representing standard deviations. (C) Secondary structure model of A.n. COB pre-RNA showing positions of DEPC modification or protection. Open arrows point to splice sites. Two independent DEPC mapping experiments were performed, and positions were scored as protected on the secondary structure model if a twofold or greater reduction in modification level relative to 0 mM Mg2+ was observed in both experiments. The state of modification for unmarked positions could not be assigned because of inconsistencies between experiments, degradation, or poor resolution in the gel. For the A.n. COB intron, adenines in single-stranded regions expected to make specific contacts to orient the four domains in a catalytically active conformation include (a) the A-rich bulge in P5a with the P4 helix; (b) the J3/4 and J6/7 junctions with P6 and P4 helices, respectively; (c) the P9 loop with the P5 helix; (d) the J4/5, J5/4, and J8/7 junctions with the 5′ SS containing P1 helix; and (e) the P2 loop with P8 helix.