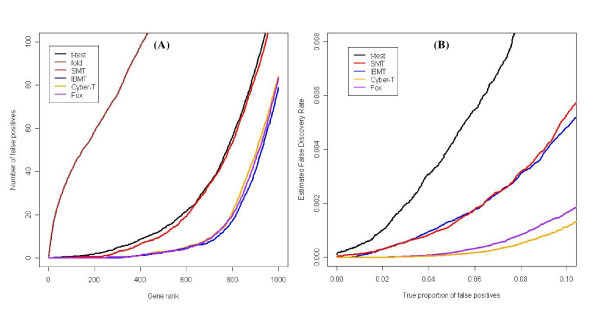
Figure 6.
Results from the Choe, et al. spike-inexperiment. (A) IBMT results in the fewest false positives overall. The other methods, from best to worst, are Fox, Cyber-T, SMT, t-test, and fold change. (B) Comparison of how accurately each method estimates the true proportion of false positives. The simple t-test performs best in correctly estimating its false positive rate, although all methods underestimate the true number of false positives, as noted in [25]. Fox's method and especially Cyber-T result in the greatest underestimation of false positives.