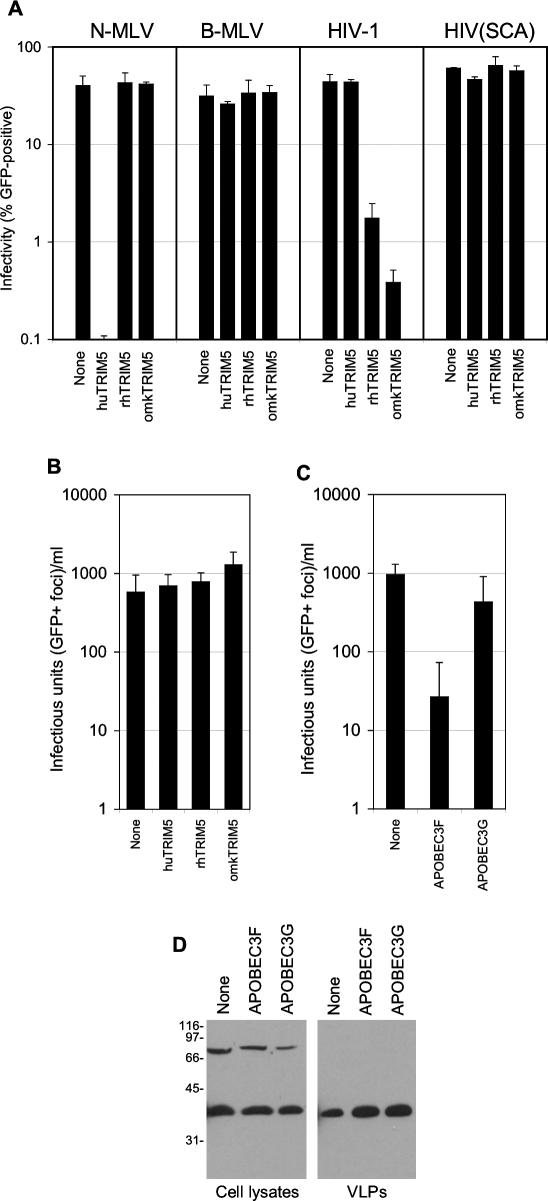
Figure 6. Effects of TRIM5 and APOBEC3 Proteins on HERV-KCON Infectivity.
(A) Unmanipulated CHO cells or variants stably expressing human TRIM5α, rhesus monkey TRIM5α, or owl monkey TRIM-Cyp were infected with VSV-G pseudotyped retroviral vectors that are sensitive to one or more of the TRIM5 proteins (N-MLV or HIV-1) or TRIM5-resistant controls (B-MLV or HIV-1 carrying SIVmac CA HIV(SCA)), as indicated. Two days postinfection, the percentage of GFP+ cells was determined using FACS.
(B) The same panel of CHO-derived TRIM5-expressing CHO cell lines were inoculated with HERV-KCON(VSV-G). Two days postinfection, GFP+ foci were quantified.
(C) APOBEC3F and APOBEC3G expression plasmids were cotransfected into 293T cells during generation of CHKCG-containing HERV-KCON(VSV-G) particles. Fresh 293T cells were infected with the resulting viral supernatant, and GFP+ foci were quantified 2 d later.
(D) Western blot analysis, using the anti–HERV-K Gag antibody, of cell and HERV-KCON virion lysates generated upon coexpression of APOBEC3F or APOBEC3G, as indicated.
All data are representative of at least three experiments.