Figure 4.
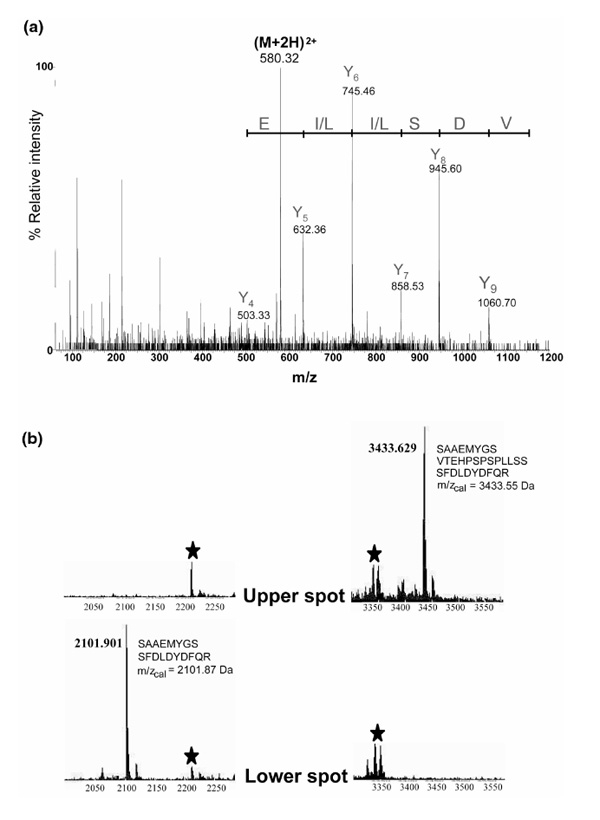
Identification of C1/C2 hnRNPs by MS and by tandem MS sequencing. (a) Collision-induced dissociation spectrum of a doubly charged ion at m/z 580.32 Da corresponding to the sequence 207-216 (VDSLLENLEK) of the C2 hnRNP. The Y ion signal series is shown together with the deduced sequence giving the peptide sequence tag (632.36)LLSD(1060.70). (b) Two sections of the MALDI-MS peptide-mass maps showing the difference between the upper (C2) hnRNP and the lower (C1) hnRNP spots excised from 2D gels (cf Fig. 3c). The signal at m/z 3433.6 Da detected in the trypsin-digested material from the upper spot could be identified as the tryptic peptide that includes the 13-amino-acid insert in C2 hnRNP (illustrated in the figure). Only the corresponding peptide without the insert could be detected (at m/z 2101.9 Da) in the peptide-mass map from the lower spot. Signals derived by autoproteolysis of trypsin are marked with stars.
