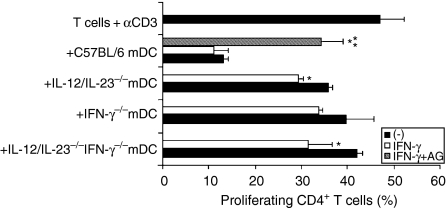
Figure 6.
Effects of interferon-γ (IFN-γ) and aminoguanidine (AG) on the modulation of T-cell proliferation by mature dendritic cells (mDCs) from interleukin (IL)-12/IL-23−/−, IFN-γ−/−, IL-12/IL-23−/− IFN-γ−/− and C57BL/6 mice. CD4+ T cells, purified from the spleen of C57BL/6 mice by using anti-CD4 magnetic beads, were stained with 5,6-carboxy-succinimidyl-fluorescein-ester (CSFE). CD4+ T cells (106) were then cultured with plate-bound monoclonal anti-CD3 (5 µg/ml) in the presence or absence (control) of mDCs (105). The mDC : CD4+ T-cell cultures were treated with recombinant IFN-γ (rIFN-γ) (2·5 ng/ml) and/or AG (0·1 mm). The proliferation of gated CD4+ T cells was determined by analysing the CSFE fluorescence intensity by using a flow cytometer. Experiments were repeated twice, with the same pattern of results obtained on each occasion. Data represent the mean values ± standard deviation (SD) of a representative experiment. SD values were calculated from triplicate samples. *P ≤ 0·05 versus untreated cells. **P ≤ 0·05 versus rIFN-γ-treated cells.