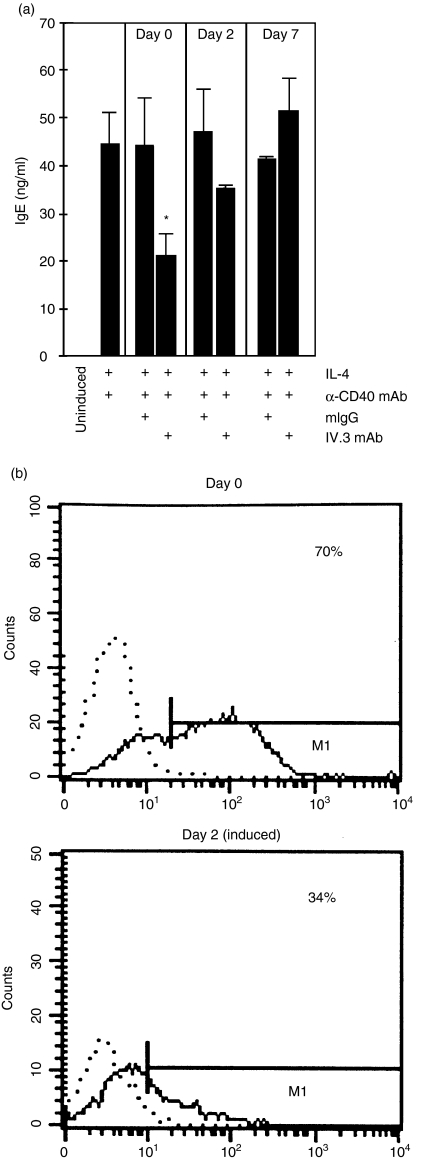
Figure 3.
Loss of the inhibitory effect of CD32 at later time-points is caused by the down-regulation of CD32 expression. (a) Tonsillar B cells were cultured with interleukin-4 (IL-4)/anti-CD40 monoclonal antibody (mAb) for 9 days, starting on day 0. A total of 10 µg/ml mouse immunoglobulin G (IgG) (mIgG) or IV.3 antibody was added on days 0, 2 or 7. Immunoglobulin E (IgE) production was measured in the cell supernatants by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). (b) Loss of CD32 surface expression upon cell culture, as measured by fluorescence-activated cell sorter (FACS) analysis. The reactivity profile against an isotype-matched control antibody (dotted line) and for the IV.3 mAb (normal line) is shown. The number denotes the percentage of IV.3-reactive cells. The data were analysed for statistical significance by using the Student's t-test (*P < 0·05).