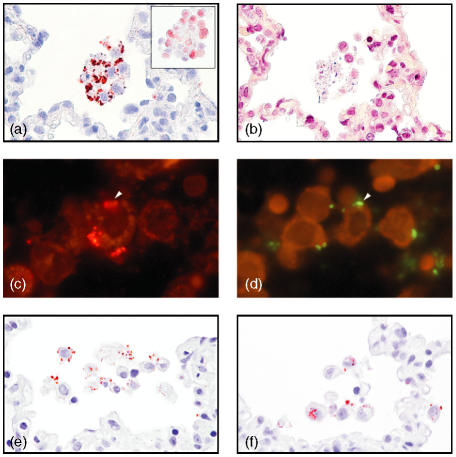
Figure 2.
Co-localization of porcine surfactant protein D (pSP-D), alveolar macrophages and bacteria. (a) In Staphylococcus aureus pneumonia, pSP-D was found to be localized in a patchy distribution on the membranes of alveolar macrophages, which show no signs of apoptosis/necrosis (magnification ×250, oil). The alveolar macrophages are identified by morphology and by hL1 immunoreactivity (insert) (magnification ×250, oil). (b) In a serial section, Gram-positive bacteria localized near these alveolar macrophages (magnification × 250, oil). (c) Immunofluorescent pSP-D and (d) Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae detected by fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) localized in serial sections on the same alveolar macrophage (arrowhead) (approximate magnification ×400, oil). pSP-D immunoreactivity as round structures (e) extracellular and (f) intracellular in alveolar macrophages in areas with acute infection (magnification ×250, oil). Detection in panels (a), (e) and (f) was carried out by using amino-ethyl-carbazole (AEC), in (b) by using a modified Gram stain, in (c) by using Cy3, and in (d) by using fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-labelled oligonucleotide probe. (a) (e) and (f) were counterstained with Mayers's hematoxylin.