Figure 1.
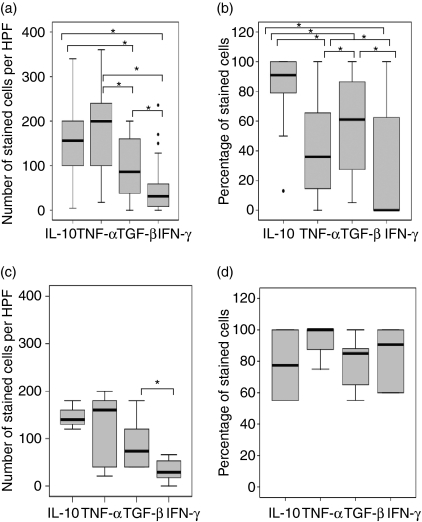
In situ distribution of interleukin-10 (IL-10), tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) and interferon-γ (IFN-γ) in the tuberculosis (TB) (a,b) and foreign body (FB) (c,d) granulomas analysed by using immunohistochemical staining. The median, 25th and 75th percentiles, and minimum and maximum values are shown. The marks  indicate the extreme values. The Wilcoxon signed-rank test was used for matched analysis and the Mann–Whitney test for two independent group comparisons. Statistical significance with a P-value of <0·05 is marked with an asterisk. (a)Number of stained cells per high power field (HPF) in the epithelioid cells within TB granulomas. There was no significant difference in the expression of TNF-α and IL-10. More cells stained positive for these two cytokines than for TGF-β; however, more cells stained positive for TGF-β than for IFN-γ. (b)Percentage of stained cells in multinucleated giant cells in TB granulomas. A higher percentage of giant cells expressed IL-10 than expressed TNF-α, TGF-β or IFN-γ. A significantly higher percentage of giant cells expressed TGF-β than TNF-α or IFN-γ. A significantly lower percentage of giant cells expressed IFN-γ than TNF-α. (c)Number of stained cells per HPF in the epithelioid cells of FB granulomas. A higher percentage of cells expressed TGF-β than IFN-γ. (d)Percentage of stained cells in multinucleated giant cells in FB granulomas. The expression of cytokines was not significantly different. TB giant cells have significantly lower percentages of TNF-α and IFN-γ as compared with FB giant cells.
indicate the extreme values. The Wilcoxon signed-rank test was used for matched analysis and the Mann–Whitney test for two independent group comparisons. Statistical significance with a P-value of <0·05 is marked with an asterisk. (a)Number of stained cells per high power field (HPF) in the epithelioid cells within TB granulomas. There was no significant difference in the expression of TNF-α and IL-10. More cells stained positive for these two cytokines than for TGF-β; however, more cells stained positive for TGF-β than for IFN-γ. (b)Percentage of stained cells in multinucleated giant cells in TB granulomas. A higher percentage of giant cells expressed IL-10 than expressed TNF-α, TGF-β or IFN-γ. A significantly higher percentage of giant cells expressed TGF-β than TNF-α or IFN-γ. A significantly lower percentage of giant cells expressed IFN-γ than TNF-α. (c)Number of stained cells per HPF in the epithelioid cells of FB granulomas. A higher percentage of cells expressed TGF-β than IFN-γ. (d)Percentage of stained cells in multinucleated giant cells in FB granulomas. The expression of cytokines was not significantly different. TB giant cells have significantly lower percentages of TNF-α and IFN-γ as compared with FB giant cells.