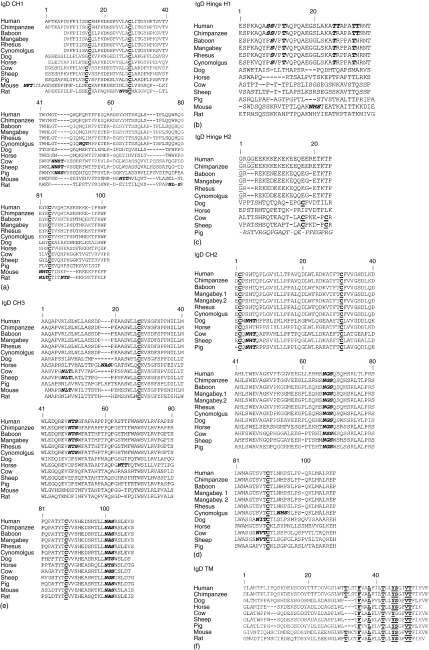
Figure 2.
Alignment of IgD heavy chain deduced amino acid sequences for each domain: CH1 (a), hinge H1 (b) and H2 (c), CH2 (d), CH3 (e) and transmembrane (f). Mouse and rat hinge is encoded by a single exon. Pig H2 is spliced out of the mature mRNA and its deduced sequence is denoted in italics to reflect this.37 (b) Glycines in the middle of the hinge, potentially contributing to flexibility, are underlined. O-glycan sites in human H1 and the corresponding conserved residues in non-human primates are bolded and italicized. (a, c, d, and e) N-glycosylation motifs (NXS or NXT where X is not proline) are bolded and italicized. Cysteines that form disulphide bonds within immunoglobulin domains and between immunoglobulin chains are bolded and underlined. (f) Amino acid of the conserved antigen receptor transmembrane motif (CART) are underlined and bolded. Mangabey.1 and mangabey.2 in D are two sequence variants. Numbering is based on the IMGT numbering for human IgD heavy chain and disregards insertions and deletions found in other species. GenBank accession numbers are given in the methods sections.