Figure 5.
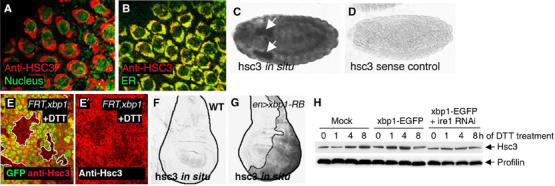
Hsc3 is an ER chaperone regulated by the Ire-1/Xbp1 pathway. (A, B) Hsc3 localizes to the ER. (A) Co-labeling with Hsc3 (red) and the nuclear membrane marker, wheat germ agglutinin (green), shows perinuclear labeling. (B) Co-labeling with the ER-YFP marker (green) shows colocalization of Hsc3 to the ER compartment (genotype: sqh-ER-YFP). (C, D) hsc3 in situ hybridization in embryos. (C) hsc3 in situ signal in embryos. Arrows point to salivary glands. (D) hsc3 sense control does not label under identical conditions. (E) Hsc3 induction by DTT requires xbp1. An eye imaginal discs with eyeless-Flipase-induced clones of xbp1−/− are labeled by the absence of GFP (green) and outlined (white boundary) (genotype: eyFLP; FRT42D xbp1k13803/FRT42DubiGFP). The discs were treated with 5 mM DTT (in S2 cells medium) for 16 h. Upregulation of Hsc3 (red) occurs in the wild-type tissue but not in xbp1 mutant tissue. (F) In situ hybridization for hsc3 in wild-type wing imaginal discs. (G) hsc3 mRNA levels are enhanced in discs expressing xbp1-RB in the posterior compartment (right half of the disc and outlined; genotype: engrailed-Gal4/uas-xbp1-RB; tub-Gal80ts: induced at 29°C for 18 h). (H) Hsc3 induction by DTT treatment requires ire-1. The upper panel shows anti-Hsc3 Western blot, whereas the lower panel shows anti-Profilin as a loading control. While Hsc3 is induced by DTT in nontransfected or xbp1-EGFP-transfected cells, pretreatment of ire-1 dsRNA blocks Hsc3 induction.
