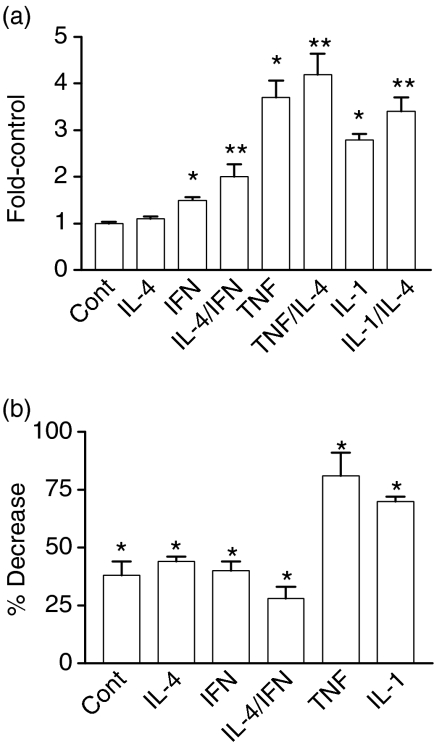
Figure 7.
Cytokine-dependent activation of NF-κB as measured using reporter gene constructs. (a) HT29 cells were cotransfected with CMV-β gal (transfection efficiency control) and NFKB-SEAP as described in Materials and Methods. Four hours later medium with the indicated cytokine(s) was added to the cells: IL-4, TNF-α, and IL-1β, each 10 ng/ml; IFN-γ, 200 U/ml. Cultures were incubated for an additional 18–20 hr. Culture medium was harvested for SEAP assays and cells were assayed for β -galactosidase activity. SEAP activity was normalized to β -galactosidase activity. To combine data from multiple experiments, the fold increase over control, where control values were for unstimulated cells, was determined. Values represent the mean ± SEM for combined data (n ≥ 9; *P < 0.001 relative to controls; **P < 0.05 for cultures treated with IL-4 and the indicated cytokine relative to the indicated cytokine alone). (b) HT29 cells were cotransfected with CMV-β gal, NFKB-SEAP, and 100 MOI of an adenoviral vector expressing β -galactosidase (LacZ) or IκBα-serine mutant (IκB) overnight. Medium without (Cont) or with the indicated cytokine was then added and cultures were incubated for 18 hr at 37°. The percent decrease in NF-κB activation for AdIκB-serine mutant-transfected cells relative to LacZ-transfected cells was then determined. Values represent the mean ± SEM, n = 12. A significant decrease was observed with the IκBα-serine mutant relative to the LacZ control; *P < 0.001.