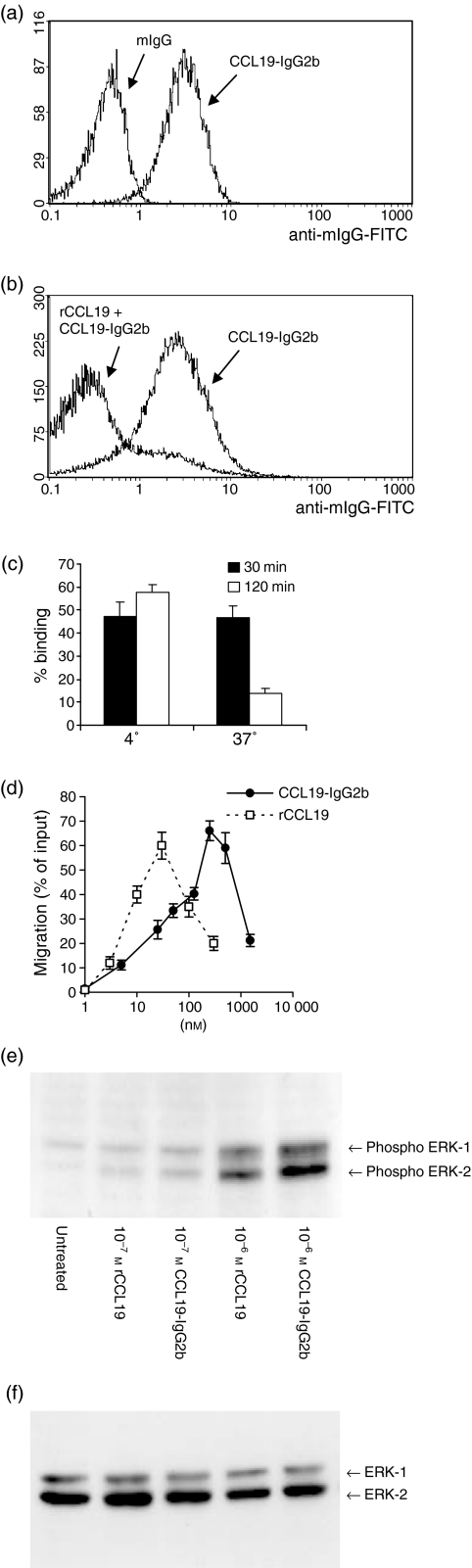
Figure 1.
Binding of CCL19-IgG2b to CCR7+ HUT78 cells and chemotactic activity. (a) Cells were incubated either with murine IgG (control) or CCL19-IgG2b (100 nm) followed by antimIgG-FITC-antibody. (b) Cells were preincubated with 100 nm recombinant CCL19 before staining with CCL19-IgG2b and anti-mIgG-FITC. (c) CCR7 is down-regulated by binding of CCL19-IgG2b in a temperature-dependent manner. FACS analysis of HUT78 cells after incubation with the CCL19-IgG2b fusion protein for the indicated times. Binding of fusion protein was detected by staining with α-murine IgG-FITC antibody. (d) Chemotactic responses of CCR7-expressing cells to rCCL19 and CCL19-IgG2b. HUT78 cells are stimulated with indicated concentrations of rCCL19, respectively, CCL19-IgG2b by using a 24-well Transwell chemotaxis chamber. The assay was done in triplicate. Shown is the percentage of migrated cells ± SD. (e) Effects of CCL19 on MAPK activation. Freshly isolated murine T cells were treated with rCCL19 or CCL19-IgG2b (10−7 and 10−6 m) at 37° for 5 min. The activity of MAPKs (ERK-2 and ERK-1 are indicated) was measured by specific phosphorylation. (f) As control for sample variations the blot was stripped according to the manufacturer's instructions (Amersham) and reprobed with p44/42 MAPK antibody, which detects total MAPK status independent of its phosphorylation, showing equal protein levels of ERK-2 and ERK-1.