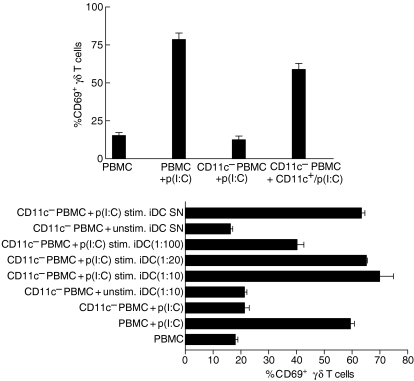
Figure 6.
Soluble factors from CD11c+ dendritic cells (DC) are responsible for the polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid [poly(I:C)]-induced activation of γδ T cells. (a) Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) were depleted from CD11c+ cells by magnetic-activated cell sorting (MACS). The negative selected cell population contained < 0·1% CD11c-expressing cells. Expression of CD69 on γδ T cells within undepleted PBMC (PBMC) or CD11c+-depleted (CD11c–) PBMC was determined after 24 hr of stimulation with 50 µg/ml poly(I:C) [p(I:C)] by two-colour fluorescence-activated cell sorter (FACS) analysis. The positive selected cell population (CD11c+) was incubated with 50 µg/ml poly(I:C) for 12 hr [CD11c+/p(I:C)], extensively washed and then incubated with CD11c– PBMC, for an additional 24 hr, at a ratio of 1 : 1. The results are shown as mean ± standard deviation (SD) of triplicate cultures from one representative donor. (b) Immature DC (iDC) were incubated with medium only (unstim. iDC) or with 50 µg/ml poly(I:C) [p(I:C) stim. iDC] for 12 hr. Afterwards, the supernatant (SN) from these iDC or extensively washed iDC were incubated with CD11c− PBMC, at the indicated ratios, for 24 hr, and expression of CD69 on γδ T cells was determined by two-colour FACS analysis. Results are shown as mean ± SD of triplicate cultures from one representative donor. Similar results were observed in two additional donors. Isopentenylpyrophosphate (IPP), phytohaemagglutinin (PHA) and phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA).