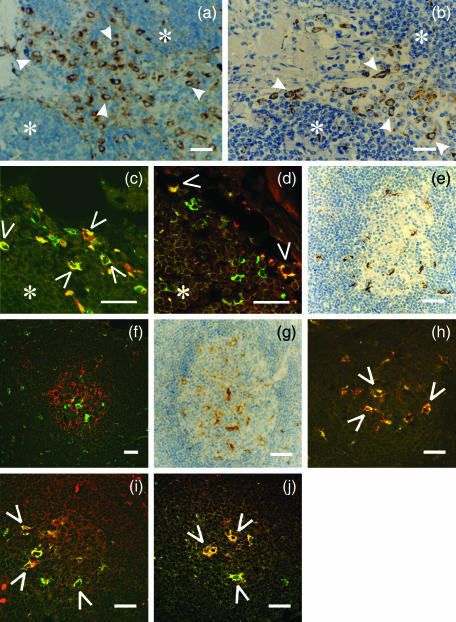
Figure 4.
Co-localization study of inhibitory p41 invariant chain with cathepsins H, L and S in sinuses with afferent lymph (a–d) and in germinal centres (e–j). Human lymph node tissue sections were labelled with different (primary) antibodies: (a) anti-cathepsin S 1E3 mAb (b) anti-cathepsin L pAb (c) anti-p41 Ii 2C12 mAb (green) and anti-CD68 mAb (red) (d) anti-p41 Ii 2C12 mAb (green) and anti-cathepsin H 1D10 mAb (red) (e) anti-CD 68 mAb (f) anti-p41 Ii 2C12 mAb (green) and anti-follicular dendritic cell mAb (red)(g) anti-cathepsin S 1E3 mAb (h) anti-p41 Ii 2C12 mAb (green) and anti-CD 68 mAb (red)(i) anti-p41 Ii 2C12 mAb (red) and anti-cathepsin L pAb (green) (j) anti-p41 Ii 2C12 mAb (green) and anti-cathepsin H 1D10 mAb (red). HRP-labelled secondary antibody was applied in a, b, e and g. Specific signal from primary Alexa Fluor™ 488-labelled 2C12 mAb (green) is shown in c, d, f, h, j, whereas Alexa Fluor™-labelled secondary antibodies were applied with all other primary antibodies (listed above). Before merging the confocal images (c, d, f, h, i and j) the signals for red fluorescence (from Alexa Fluor™ 546) and green fluorescence (from Alexa Fluor™ 488) were adjusted to comparable levels. Yellow colour (open arrows) indicates colocalization of two labelled antigens. (*) cortex. Bars: 25 µm.