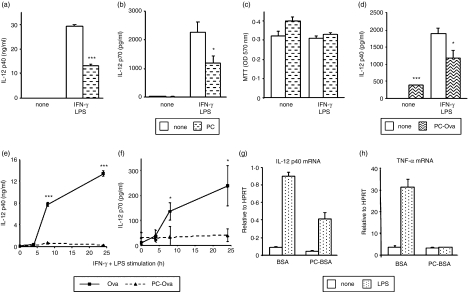
Figure 4.
Modulation of macrophage IL-12 production by in vivo exposure to PC. Peritoneal macrophages (a–c) and bmMφs (d) were pretreated with 2 μg/ml PC (a–c) or 10 μg/ml PC-Ova (d) for 18 hr prior to stimulation with 100 U/ml IFN-γ and 100 ng/ml S. minnesota LPS. IL-12 p40 and bioactive p70 levels in 24-hr culture supernatants were determined by ELISA (a, b, d). ELISA data are presented as mean plus standard deviation; *P < 0·05, ***P < 0·005 compared to non-PC treatment. Cell viability following treatment was assessed by MTT assay (c). In (e) and (f), mice were exposed to PC-Ova or Ova (0·05 μg/hr) by constant release from osmotic pumps for 2 weeks. Peritoneal macrophages were then isolated and stimulated with 100 U/ml IFN-γ and 100 ng/ml S. minnesota LPS for the times indicated. IL-12 p40 and bioactive p70 levels in culture supernatants were determined by ELISA. Data are presented as mean plus standard deviation; *P < 0·05, ***P < 0·005 compared to Ova treatment. In (g) and (h) bmDCs derived ex vivo from mice exposed to PC-BSA or BSA (0·05 μg/hr) by constant release from osmotic pumps for 2 weeks were stimulated with 1 μg/ml E. coli LPS for 8 hr. IL-12 p40 and TNF-α mRNA levels were determined by TaqMan real-time RT-PCR and are expressed relative to HPRT mRNA. Results are representative of at least two experiments.