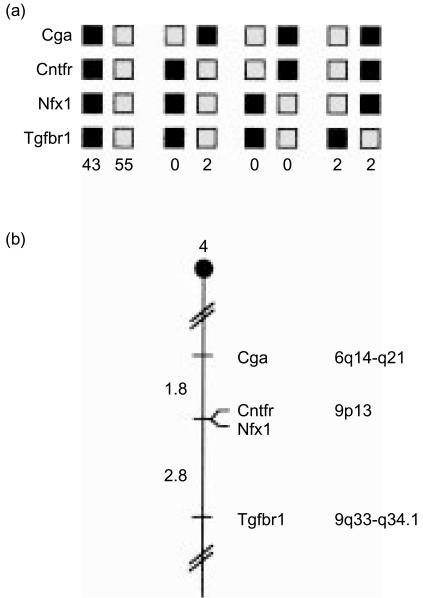
Figure 2.
(a) m-Nfx.1 maps in the proximal region of mouse chromosome 4. m-Nfx.1 was placed on mouse chromosome 4 by interspecific backcross analysis. The segregation patterns of m-Nfx.1 and flanking genes in 104 backcross animals that were typed for all loci are shown. For individual pairs of loci, more than 104 animals were typed (see text). Each column represents the chromosome identified in the backcross progeny that was inherited from the (C57BL/6J×Mus spretus)F1 parent. The shaded boxes represent the presence of a C57BL/6J allele and the white boxes represent the presence of an M. spretus allele. The number of offspring inheriting each type of chromosome is listed at the bottom of each column. (b) Partial chromosome 4 linkage map showing the location of murine m-Nfx.1 in relation to linked genes. Recombination distances between loci [in centimorgans (cM)] are shown to the left of the chromosome and the positions of loci in human chromosomes, where known, are shown to the right. References for the human map positions of loci cited in this study can be obtained from Genome Database (GDB), a computerized database of human linkage information maintained by the William H. Welch Medical Library of The Johns Hopkins University (Baltimore, MD). (c) Schematic of mouse chromosome 4 showing the location of m-Nfx.1 (arrow) relative to a larger number of known genes. Corresponding locations for each gene in human chromosomes are indicated to the left.