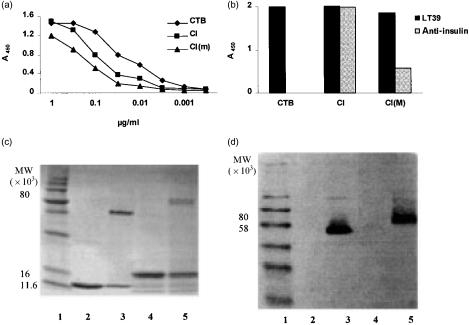
Figure 2.
Characterization of CI and CI(m) fusion proteins by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and sodium dodecyl sulphate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS–PAGE). (a) Reactivity of CI and CI(m) proteins with GM1 ganglioside and antibody to the B-subunit of cholera toxin (CTB) in GM1-ELISA in comparison with a native CTB control. The concentrations of the CI and CI(m) samples were initially adjusted as described in the text. The samples were serially diluted using threefold dilutions and incubated for 1 hr prior to addition of the CTB-specific monoclonal antibody (mAb) LT39. (b) Reactivity of CTB and the CI and CI(m) proteins, with respect to LT39 and anti-insulin mAbs, was tested by ELISA. The protein concentrations were adjusted to ≈ 1 µg/ml and used to coat microtitre plates directly (without prior coating with GM1), otherwise treatment with the primary and secondary antibodies and development were as described in the Materials and methods. (c) SDS–PAGE (15%) analysis of CI protein compared with native CTB. The concentration of SDS used in the gel and the sample preparation buffers was reduced to 50% of the concentrations normally used. Both boiled and non-boiled samples of each protein were loaded. Lanes: 1, molecular weight standard; 2, CTB (5 µg), boiled; 3, CTB, non-boiled; 4, CI protein (≈ 5 µg), boiled; 5, CI protein (≈5 µg), non-boiled. (d) Western blot analysis. Proteins from a similar gel as in (c) were reacted in Western blots with the CTB-specific mAb, LT39, which reacts with CTB pentamer. The lane numbering is the same as for the SDS–PAGE gel in (c).