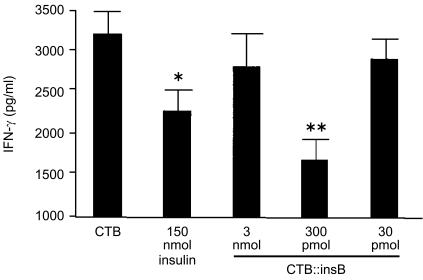
Figure 5.
Suppression of interferon-γ (IFN-γ) in mice immunized with CI fusion protein. Lymph node cells from mice (the same animals as in Exp. 2 in Fig. 4) treated with 30 pmol, 300 pmol or 3 nmol of the CI fusion protein, or with 150 nmol of insulin (animals from Exp. 2 in Fig. 4) were stimulated with ovalbumin (OVA) for 72 hr and the supernatant was harvested and analysed for the level of IFN-γ production by sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Asterisks denote a statistically significant difference from cholera toxin B (CTB)-treated mice, *P<0·05, **P<0·01. Data represent the mean value obtained from quadruplicate cultures (±1 SD).