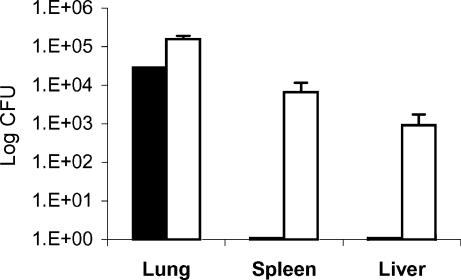
Figure 7.
Comparison of bacterial burden in lung, spleen and liver of mice following reactivation versus primary infection. C57BL/6 mice were infected with 30 colony-forming units (CFU) of Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv and the number of viable CFU was determined 2 weeks postinfection (solid bars). Mice were then treated with rifampicin and isoniazid (RMP-INH) for 8 weeks to achieve latency (with no viable bacilli detected in all organs). After 20 weeks in this latent state, a group of mice received 2·5% aminoguanidine containing 10% glucose in drinking water ad libitum to induce reactivation. The increases in bacterial count following reactivated infection are shown 2 weeks after aminoguanidine administration (open bars). Results are expressed as means ± SEM and are representative of three independent experiments with four mice per group per time-point.