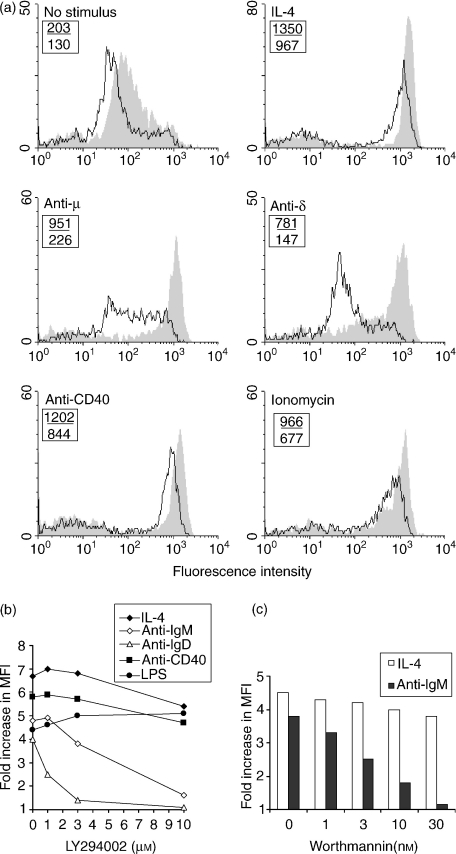
Figure 3.
Effects of LY294002 and wortmannin on the ability of various stimuli to induce major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II upregulation. (a) BALB/c B cells, treated as described in the legend to Fig. 2, were cultured with the indicated stimuli [anti-immunoglobulin D (anti-IgD), 20 µg/ml; ionomycin, 0·3 µm; anti-CD40, 5 µg/ml; concentrations of the other stimuli were as stated in the legend to Fig. 2] with (–) or without (shaded) LY294002 (10 µm). The data shown represent the fluorescence on 10 000 cells per sample. The numbers shown in the upper left of each histogram represent the mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of MHC class II fluorescence in the presence (lower value) or absence (upper value) of inhibitor. Similar results were obtained in two other, similar, experiments. (b) BALB/c B cells pretreated with the indicated concentrations of LY294002 were cultured at 2 × 106 cells/ml for 24 hr with the indicated stimuli [lipopolysaccharide (LPS), 10 µg/ml; concentrations of the other stimuli were as stated in the legend to Fig. 2] before being harvested for staining and fluorescence-activated cell sorter (FACS) analysis. The data represent the fold increases in the MFI of MHC class II staining compared with those seen for control cells cultured without stimulation, and are representative of two similar experiments. (c) BALB/c B cells, precultured with the indicated concentrations of wortmannin, were further cultured for 24 hr in the presence of F(ab′)2 anti-µ (5 µg/ml) or interleukin-4 (IL-4) (50 U/ml) before expression of MHC class II was examined by staining and FACS analysis. The data shown represent the fold increase in MFI of MHC class II staining over that seen for cells cultured without stimulation. Similar results were obtained in two other experiments. The Student's t-test was used to compare the MFIs of untreated cells stimulated with IL-4 or anti-IgM with those of cells treated with the indicated concentrations of inhibitor. For IL-4 stimulation, the MFI of cells treated with 1, 3 or 10 nm wortmannin was not significantly different from that of control cells, at 30 nm the difference was just significant (P = 0·04). For anti-IgM stimulation, the differences were significant at all inhibitor concentrations (P < 0·0002).