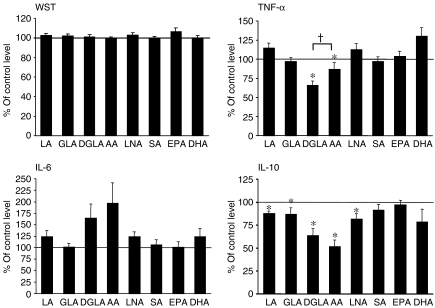
Figure 3.
The effect of n-3 and n-6 fatty acids on the viability and cytokine levels of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) in vitro. Cells were incubated in the presence of 100 µm of the respective fatty acid, and cytokine levels were measured 20 hr after the induction of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) stimulation, as described in the Materials and methods. Cell viability (determined using the WST-1 assay) was measured during the final 5 hr of LPS stimulation, as described in the Materials and methods. The mean values (of triplicate measurements) ± standard error of the mean (SEM), from 12 blood donors, are shown. Control incubations were cells incubated with 100 µm control fat blend (Table 1), and the cytokine levels of controls were as follows: 1349 ± 251 pg/ml tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α); 6576 ± 2082 pg/ml interleukin (IL)-6; and 437 ± 55 pg/ml IL-10. *P < 0·05 versus control incubations. †P < 0·05 for dihomo-γ-linolenic acid (20:3n-6) (DGLA) versus arachidonic acid (AA) (one-tailed Student's t-test).