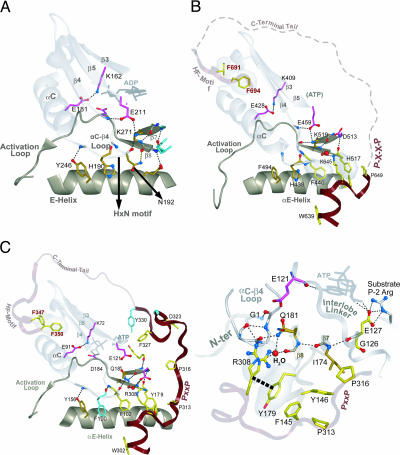
Fig. 4.
Comparison of interlobe interactions in non-AGC kinases (Aurora, A) and AGC kinases [PKC (B) and PKA (C)]. Main-chain traces of key regions are colored as indicated at the top of Fig. 1). Main-chain traces of phosphate moieties use the standard CPK color scheme). Oxygen, nitrogen, and hydrogen atoms establishing hydrogen bonds are red, blue, and white, respectively). Side chains of kinase-shared residues are pale magenta. Side chains of residues shared between Eukaryotic and Eukaryotic-like kinases are shown in gold (29). AGC-specific residues are in light yellow. Hydrogen bonds are depicted as dotted lines. CH–π interactions are depicted as dotted lines into dot clouds. (A) Canonical EPK interactions in the interlobe region of Aurora kinase, which does not belong to the AGC group. (B and C) Conserved interactions between the CLT and the interlobe region of PKC (B) and PKA (C) that belong to the AGC group. A close-in view of PKA interactions are shown in C Right. The role of only one of the conserved residues in the AST is known to play a role in PKA function, a phenylalanine (F327PKA), that acts as a gate for and assists in ATP binding (31). Much of the PKC AST region is disordered in the crystal structure; this region is represented by a dotted line. Water molecule is shown in red spheres representation (B and C) and labeled H2O in C.