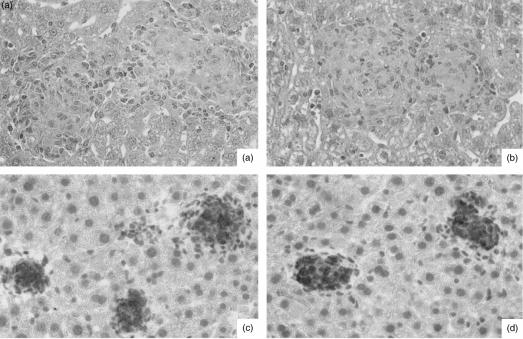
Figure 6.
Comparative liver histopathology in Mycobacterium avium-infected CD14+/+ (wild type) and CD14-deficient (−/−) mice. CD14+/+ (a) and (c) and CD14−/− (b) and (d) mice were infected intravenously with either 1 × 105 colony-forming units (CFU) of M. avium TMC724 (a) and (b), or 1 × 105 CFU of M. avium SE01 (c) and (d), and killed 5 weeks (a) and (b) or 8 weeks (c) and (d) postinfection for histological analysis of the liver. (a) and (b) Well-structured granulomas with epithelioid macrophages (haematoxylin & eosin staining; magnification ×128). (c) and (d) Circumscript inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS)-positive granulomas (immunoperoxidase staining; magnification × 128).