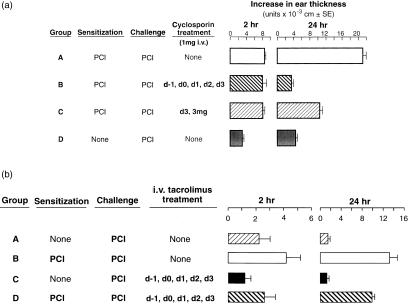
Figure 1.
Effects of systemic treatment with cyclosporin (CsA) and tacrolimus on the early and late components of PCl CS. (a) Intravenous CsA inhibits the late component of PCl CS but not the early component. CBA mice were contact sensitized with 5% PCl on day 0. Four days later CS responses were elicited by challenging the ears with 0·8% PCl. Mice were treated daily with 1 mg CsA in PBS (pH 7·2) i.v. on day −1 through to day +3 (Group B), or with vehicle alone on day −1 to day +3 (Group A), or with 3 mg i.v. just on day +3 (Group C). Ear thickness was quantified prior to challenge, and at 2 and 24 hr following challenge. Controls were not immunized nor treated with CsA, but were just challenged on the ears with PCl (Group D). P < 0·001 for Group B versus A and P < 0·005 for Group C versus A, at 24 hr. (b) Intravenous treatment with tacrolimus suppresses both early and late PCl CS responses. CBA mice were sensitized with PCl and 4 days later their ears were challenged with 0·8% PCl. Groups B and D received tacrolimus at a dose of 0·02 mg/day intraperitoneal from 1 day prior to sensitization, until the day of challenge, and were compared to untreated Group C, and to Group A, that received vehicle alone. P < 0·05 Group C versus A at 2 hr, and Groups B versus D at 2 hr. P < 0·005 Group C versus A and Group B versus D, at 24 hr.