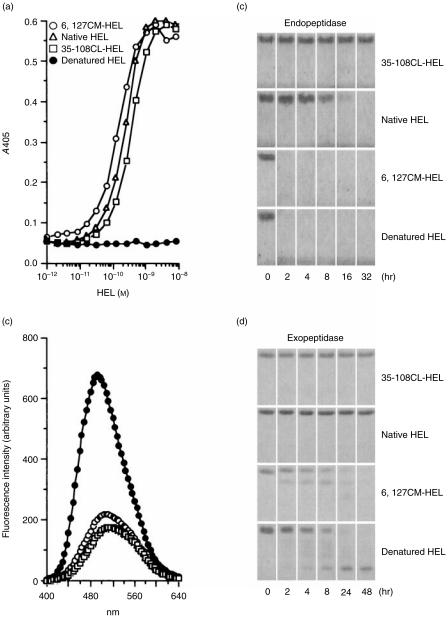
Figure 2.
The structural profiles of hen-egg lysozyme (HEL) derivatives. (a) Detection of the tertiary conformation of HEL by sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Two different monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), recognizing different conformational epitopes of HEL, were used according to the procedure described in the Materials and Methods. (b) Binding of 8-anilino-1-naphthalenesulphonic acid (ANS) to HEL derivatives. The different HEL derivatives shown on the figure were incubated with ANS at 37° and pH 7·5. After a 10-min incubation, the fluorescence spectra (400–640 nm) were measured by excitation at 372 nm. The control spectrum was measured under the same experimental conditions but in the absence of HEL. The spectra of native HEL and 35–108CL-HEL were almost the same as that of the control spectrum. (c) and (d) Susceptibility of HEL derivatives to proteolysis. HEL derivatives were digested with alpha-chymotrypsin (c) and carboxypeptidase Y (d) at 37° and pH 7·5. Each incubation was terminated at various time-points and the digested samples were stored at −20° until analysed by sodium dodecyl sulphate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS–PAGE).