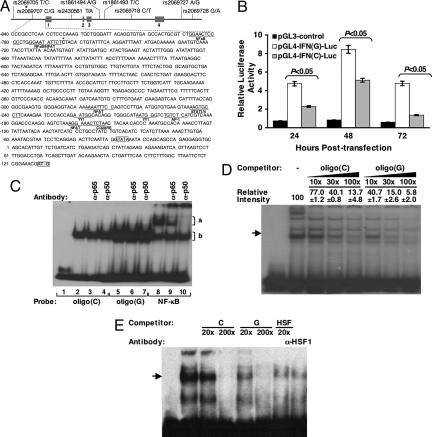
Fig. 1.
Functional analyses of SNP −764C/G in vitro. (A) The eight SNPs in the human IFN-γ gene genotyped in this study are shown with their IDs and the corresponding polymorphic bases. The four exons are represented as boxes. Sequence of the promoter and 5′ UTR region is presented with the position number relative to the transcription site as predicted by Gray and Goeddel (35). The open and shaded boxes in the sequence represent the transcription initiative site (TATA box) and the translation start codon (AUG), respectively. The previously reported transcription factor binding sites are underlined. Asterisk indicates the SNP rs2069707. (B) Jurkat cells were cotransfected with individual firefly luciferase (FLuc)-expressing plasmid (pGL3-control, pGL4-IFN(C)-Luc, or pGL4-IFN(G)-Luc) and pRL-CMV as described in Materials and Methods. Cells were harvested after incubation for indicated periods and relative luciferase activity (FLuc/Renilla luciferase) was determined. Bars and error bars indicate mean ± SD of three experiments. (C) The 32P-labeled −764C, −764G, or NF-κB DNA oligonucleotide probe was used in the EMSA as indicated in the presence (lanes 2–10) of a HeLa cell nuclear extract in comparison with the absence of nuclear protein (lane 1). Antibodies against p65 (lanes 3, 6, and 9) and p50 (lanes 4, 7, and 10) were used for supershift assay. (D) EMSA was performed by using 32P-labeled probe containing −764C with HeLa cell nuclear extract, with or without competition from unlabeled oligonucleotides containing −764C and −764G as indicated. Relative densities of bands are shown as mean ± SD. The first lane represents the absence of nuclear extract. (E) EMSA was performed by using biotin-labeled probe containing HSF binding motif with Jurkat cell nuclear extract, with or without competition from unlabeled oligonucleotides containing −764C, −764G, HSF probe itself, or anti-HSF1 antibody as indicated. The first lane represents the absence of nuclear extract.