Figure 4.
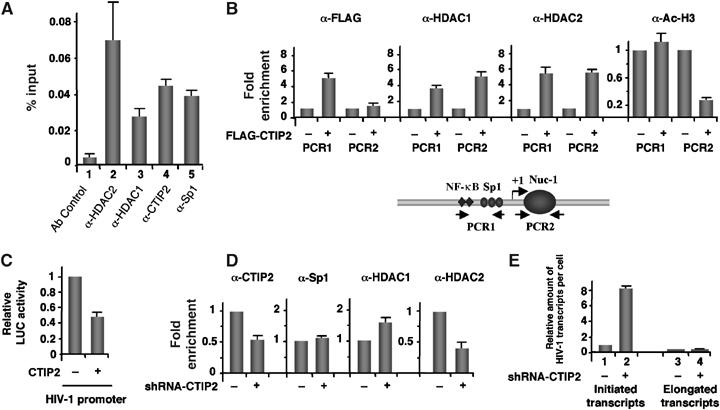
Association of CTIP2 with the HIV-1 proximal promoter induces local H3 deacetylation with concomitant recruitment of HDAC1 and HDAC2. (A, D) Microglial cells (A) and CTIP2 knockdown cells (D) were infected with the VSV-pseudotyped pNL4.3-env− virus 24 h before being subjected to ChIP experiments with the indicated antibodies. As a control, immunoprecipitations were performed in the absence of antibody (Ab control). Input (1/1000) and immunoprecipitated DNAs were quantified by real-time PCR using PCR1 LTR-specific oligonucleotides. The amount of immunoprecipitated material was normalized to the input DNA (A) and fold enrichments were normalized to the nonspecific enrichment in the GAPDH DNA (D). (B) ChIP experiments were performed on HEK 293T cells transfected with the HIV-1 LTR-LUC episomal vector in the presence or absence of the FLAG-CTIP2 expression vector as indicated. Cells were subjected to ChIP assays with the indicated antibodies. Specific enrichments in HIV LTR regions were quantitated by real-time PCR with the PCR1, PCR2 and GAPDH oligonucleotides. Results were normalized to enrichment in nonspecific GAPDH DNA. Results are representative of three independent experiments. (C) LTR-LUC-transfected HEK 293T cells were subjected to LUC activity quantification in the presence or absence of overexpressed CTIP2. (E) Initiated and elongated HIV-1 gene transcripts were quantitated by real-time RT–PCR in HIV-1-infected control and CTIP2 knockdown microglial cells. PCR quantifications target the HIV-1 TAR (initiation) and the HIV-1 Tat (elongation) regions. Results are presented relative to the initiated transcripts in control cells and normalized to β-actin copies.
