Figure 7.
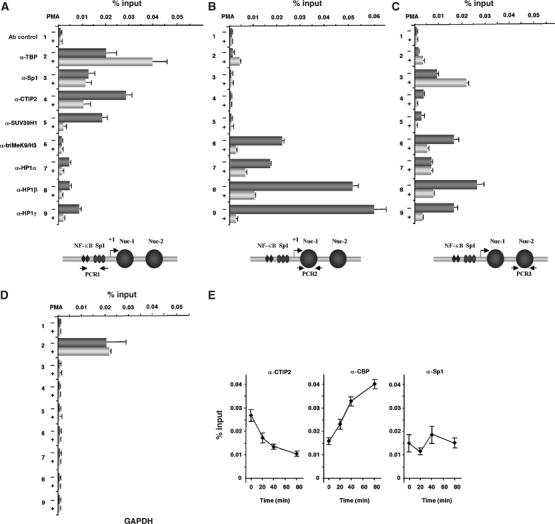
Transcriptional HIV-1 activation is accompanied by a decreased recruitment of CTIP2 and HP1 to the viral proximal promoter in the chromosomal context of integrated proviruses. ChIP assays were used to detect association of TBP, Sp1, CTIP2, HP1α, HP1β, HP1γ, triMeK9/H3 or SUV39H1 with the HIV-1 promoter proximal region (PCR1) (A), the Nuc-1-binding region (PCR2) (B), the Nuc-2-binding region (PCR3) (C) or the GAPDH promoter (D). U1 cells were mock-treated (−) or treated (+) with PMA (100 nM) for 1 h (A–D) and 20–80 min for time-ChIP assays (E). The amount of immunoprecipitated material was normalized to the input DNA. (E) U1 cells were mock-treated or treated with PMA (100 nM) for the indicated times and the proteins were crosslinked with formaldehyde for 10 min and DNA sheared. The crosslinked protein/DNA complexes were immunoprecipitated with the indicated antibodies or with a purified IgG as negative control. The protein/DNA crosslinks were reversed and the purified DNA was amplified and quantified by real-time PCR using the PCR1 primer. The amount of immunoprecipitated material was normalized to the input DNA.
