Figure 1.
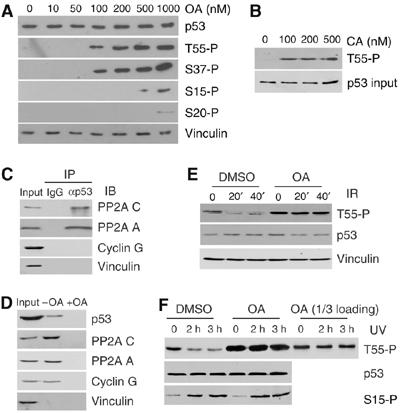
Inhibition of PP2A abolishes DNA damage-induced Thr55 dephosphorylation. (A) U2OS cells were treated with OA for 2 h at different concentrations. p53 protein as well as Thr55, Ser15, Ser37 and Ser20 phosphorylation levels were detected with the indicated antibodies. (B) Thr55 phosphorylation in cells treated with calyculin A (CA). (C) U2OS whole-cell extracts were immunoprecipitated with anti-p53 antibody and immunoblotted with anti-PP2A C, anti-PP2A A, anti-cyclin G and anti-vinculin antibodies. (D) U2OS lysates were incubated with microcystin beads in the absence (−) or presence (+) of 50 nM OA. Proteins associated with beads were analyzed by Western blot analysis with the indicated antibodies. (E, F) U2OS cells were exposed to IR (E) or UV (F) radiation in the absence (DMSO control) or presence of 200 nM okadaic acid (OA). The cells in (E) were treated with OA for 1 h and the cells in (F) were treated for 3 h. To normalize the p53 protein level, cells were treated with MG132 before irradiation. Cells were harvested after DNA damage at the times indicated and Thr55 and Ser15 phosphorylation was assayed.
