Figure 6.
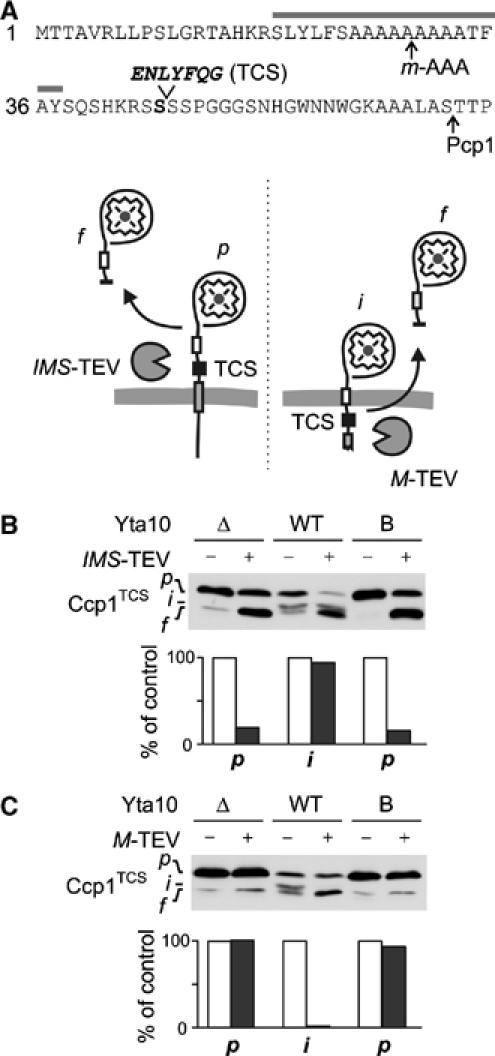
m-AAA protease dislocates the precursor of Ccp1 to the matrix. (A) The presequence of Ccp1TCS harbouring a TEV cleavage site (TCS) after S45 (Ccp1TCS). Grey bar, hydrophobic sorting signal; arrows, processing sites. Lower panel: Potential topologies of Ccp1TCS in the inner membrane and cleavage by TEV proteases located in the intermembrane (IMS-TEV) or matrix space (M-TEV). (B) Cleavage of Ccp1TCS by IMS-TEV in vivo. The precursor of Ccp1TCS accumulates in Δyta10Δpcp1Δccp1 cells (Δ), whereas the intermediate form is generated upon expression of Yta10, which at least partially complemented the processing deficiency (WT). To examine the accessibility of TCS from the intermembrane space, IMS-TEV, Yta10 (WT) and Yta10E388Q (B) were expressed when indicated and Ccp1 cleavage was monitored by immunoblotting. p, precursor form; i, intermediate form; f, proteolytic fragment produced by TEV cleavage. We observed the accumulation of a similar-sized proteolytic fragment of Ccp1TCS in some cells even in the absence of TEV, which might result from the degradation of Ccp1 molecules mislocalised to the matrix. To avoid any interference with our interpretation, we only quantified the stability of precursor (Δ, B) and intermediate forms (WT) in the presence or absence of TEV in the lower panel. Values were expressed as a per cent of precursor or intermediate form in the absence of TEV. (C) Cleavage of Ccp1TCS by M-TEV in vivo. M-TEV and Ccp1TCS were coexpressed in Δyta10Δpcp1Δccp1 cells (Δ) containing Yta10 (WT) or Yta10E388Q (B) when indicated. Ccp1 cleavage was analysed and quantified as in (B).
