Figure 3. Identification and characterization of Runt domain mutants with increased DNA binding affinity.
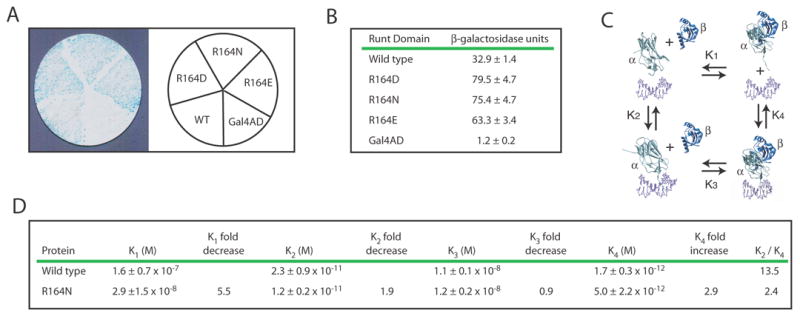
(A) β-galactosidase filter assay for three Runt domain mutants, R164N, R164D, and R164E, in the YM4271(HA-H/L) reporter strain.
(B) Results from the liquid β-galactosidase assay for R164N, R164D, and R164E. β-galactoside units are indicated ± standard deviation. The differences in activity between these mutants and the wild-type Runt domain were significant at P = 0.00001 for R164N, P = 0.00005 for R164D, and P = 0.00001 for R164E.
(C) Thermodynamic box illustrating the dissociation constants (K1, K2, K3, K4) for the interactions between the Runt domain (α), CBFβ (β), and the DNA (unlabeled, purple).
(D) Equilibrium dissociation constants for the wild-type Runt domain and the R164N mutant. The P values for the differences in K2 and K4 were = 0.11 and 0.06, respectively. K2/K4 represents the degree to which CBFβ enhances DNA binding by the Runt domain. Each K value was averaged from at least three binding curves.
