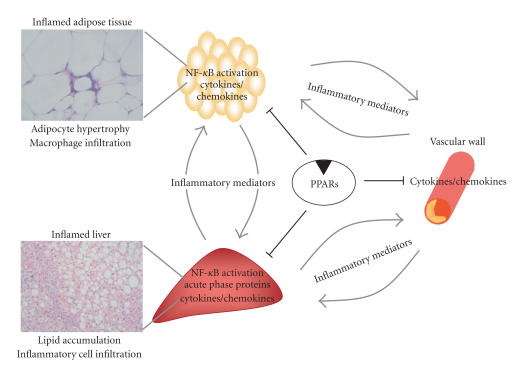
Figure 1.
Central role of PPARs in obesity-induced inflammation. (Visceral) obesity and associated fatty liver stimulate inflammation in adipose tissue and liver via increased recruitment and infiltration of macrophages, resulting in increased production of proinflammatory cytokines. By downregulating proinflammatory genes in liver, adipose tissue and the vascular wall, PPARs have a major influence on the progression of obesity-related inflammation and its complications.