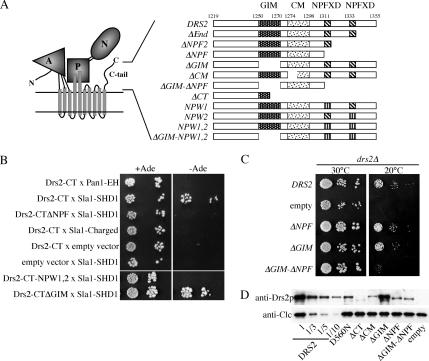
Figure 2.
C-tail sequences containing the NPFXD motifs bind Sla1p and contribute to Drs2p function. (A) Predicted topology and domain structure of Drs2p based on the crystal structure of the related sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca++ ATPase (A, actuator; P, phosphorylation; N, nucleotide binding) (Toyoshima and Inesi, 2004). Schematic diagram of motifs in the Drs2p C-tail and constructs used in this study (GIM and CM). (B) Two-hybrid test for interaction between Drs2p C-tail and Sla1p SHD1 domain. Bait and prey plasmids used are described in Table 2. Serial dilutions of the cells were spotted on minimal medium with or without adenine (Ade). Growth in the absence of adenine indicates a two-hybrid interaction. (C) Synergistic defect caused by deleting both the GIM and C-terminal 44 amino acids bearing the two NPFXD motifs. Serial dilutions of drs2Δ strains (ZHY615M2D) expressing the indicated constructs were tested for their ability to grow at 20°C. DRS2 is the wild-type gene and “empty” received the vector without an insert, thus showing the drs2Δ growth phenotype. (D) Western blot of cell lysates probed for Drs2p and clathrin light chain (Clc1p). Lysates were normalized for cell equivalents and compared with a dilution series from cells expressing wild-type DRS2.