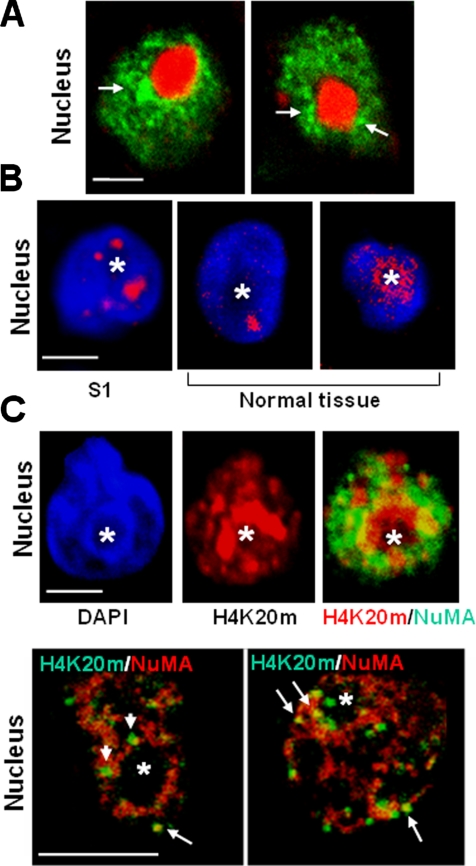
Figure 4.
In acinar cells, NuMA locates to regions enriched in heterochromatin. (A and C) S1 cells were cultured in 3D for 10 d to induce acinar differentiation. (B) S1 acini and paraffin sections of archival biopsies of normal breast tissue were used for immunostaining. (A) Immunostaining for NuMA (green) and nucleophosmin (red) in S1 acinar cells. Arrows indicate areas where NuMA concentrates around the nucleolus. (B) Immunostaining for H4K20m (red) in S1 acinar cells (S1) and luminal cells from normal breast tissue (normal tissue). Nuclei are counterstained with DAPI (blue). (C) Top, dual staining for H4K20m (red) and NuMA (green) in S1 acinar cells shows the concentration of H4K20m and NuMA domains around the nucleolus and some staining overlap (yellow). The nucleus is identified by DAPI staining (blue). The same nucleus is shown in each of the three images. Bottom, higher magnification of a dual staining for NuMA (red) and H4K20m (green) reveals that domains formed by the two proteins often intercalate around the nucleolus (see arrowheads). A few H4K20m domains colocalize with NuMA staining (as shown by yellow at arrows). One nucleus is shown per image. Bar, 2.5 μm. Asterisk indicates nucleolus.