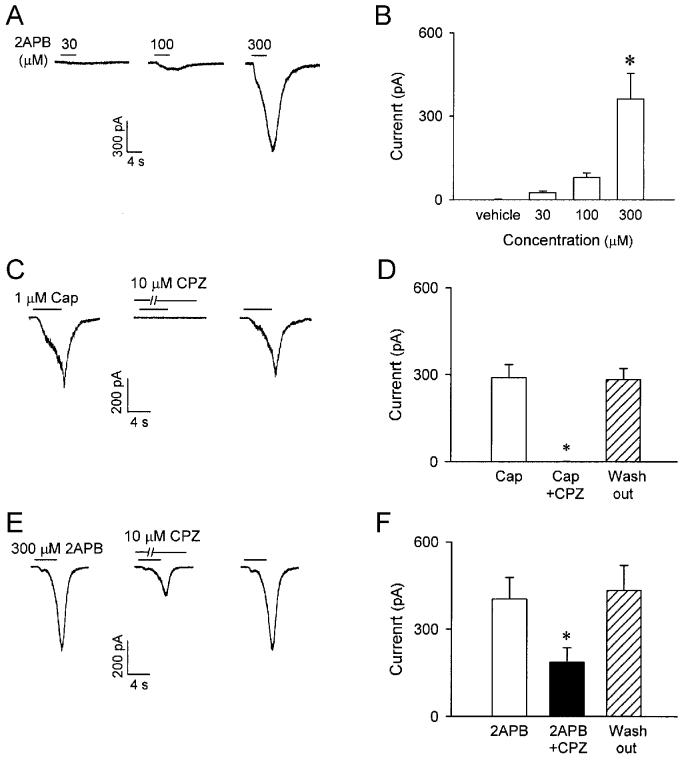
Fig. 8.
2APB-induced whole-cell inward current and effect of capsazepine on the currents induced by capsaicin and 2APB in isolated rat pulmonary capsaicin-sensitive neurons. A: experimental records illustrating that a small pulmonary nodose ganglia neuron (18.5 pF) was activated by application of three concentrations of 2APB (30, 100 and 300 μM; 4 s, added horizontal bars). B: group data showing the concentration-dependence of the whole-cell inward currents induced by 2APB (4-8 s). * Significantly different (P < 0.05) from the response to 2APB vehicle. Data are means ± SE of 14 neurons tested for each group, except the group of 300 μM (n = 24). C and E: experimental records illustrating the effect of pretreatment with capsazepine (10 μM; 5 min), a selective TRPV1 antagonist, on the inward currents induced by capsaicin (1 μM; 5 s) and 2APB (300 μM; 4 s), respectively. D and F: group data for responses to capsaicin (0.3-1 μM; 4-8 s) and 2APB (300 μM; 4-8 s), respectively, before (open bars), during (closed bars) and ∼60 min after (hatched bars) capsezepine (10 μM; 5 min). Cap, capsaicin; CPZ, capsazepine. * Significantly different (P < 0.05) from the response before capsazepine treatment. Data are means ± SE of 8 and 9 pulmonary capsaicin-sensitive neurons in D and F, respectively.