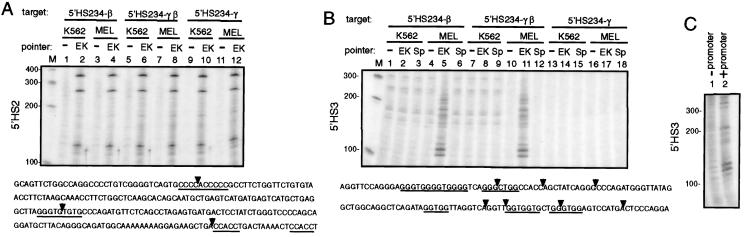
Figure 2.
The role of the β-globin promoter in EKLF pointer recruitment to the LCR. (A) Recruitment of EKLF pointer to 5′HS2 in the target plasmid, in which the LCR is linked to the β-globin promoter (lanes 1–4), the γ- and β-globin promoters in tandem (lanes 5–8), or the γ-globin promoter (lanes 9–12), was analyzed by PIN*POINT assay (as in Fig. 2) using the 5′HS2-specific primer JS90. The CACCC boxes (underlined) and the cleavage sites of the EKLF pointer (arrowhead) in 5′HS2 are shown at the bottom. (B) Recruitment of EKLF (EK) and Sp1 (Sp) pointer to 5′HS3 was analyzed by performing primer extension with 5′HS3-specific primer JS46P on the DNA samples used in A. The CACCC boxes (underlined) and cleavage sites (arrowheads) of the EKLF pointer in 5′HS3 are shown at the bottom. Because the bands created by the EKLF pointer were numerous and intensities slightly variable from experiment to experiment, only the cleavages that are most consistently seen are indicated at the bottom. (C) EKLF pointer is not recruited to 5′HS3 in the absence of a promoter in cis. The promoter in the target plasmid 5′HS234-β (+promoter, p269) was deleted and used as a target plasmid (−promoter, p388). The PIN*POINT assay was performed as in B.