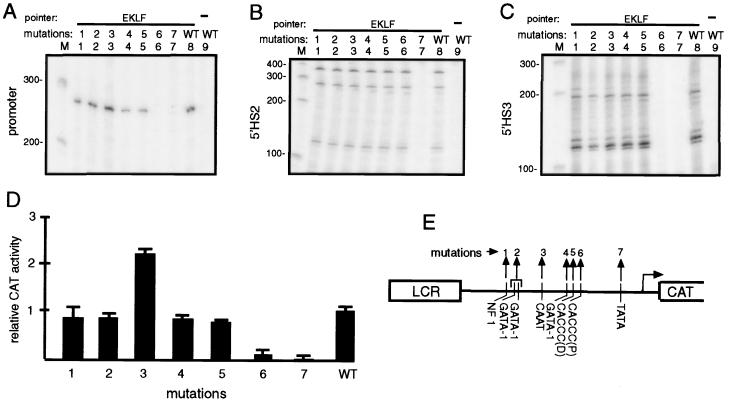
Figure 3.
The role of various promoter elements in EKLF pointer recruitment. A series of promoter-mutated target plasmids derived from 5′HS234-β (described in E) were cotransfected with EKLF pointer expression vector. Recruitment of EKLF pointer to the β-globin promoter (A), to 5′HS2 (B), and to 5′HS3 (C) of each of these target plasmids was analyzed by primer extension using primers JS41 (A), JS90 (B), and JS46P (C). Lanes 1–7 correspond to target plasmids with mutation 1–7, lane 8 to wild-type promoter, and lane 9 to no pointer expression vector. (D) The transcriptional activity of the β-globin promoter constructs containing the mutations shown in E. The target (reporter) plasmids (10 μg) were transiently transfected into MEL cells, and chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) assay was performed after 48 h. (E) The mutated transcription factor binding sites in the β-globin promoter of the target plasmids used in panels A–C are shown schematically.