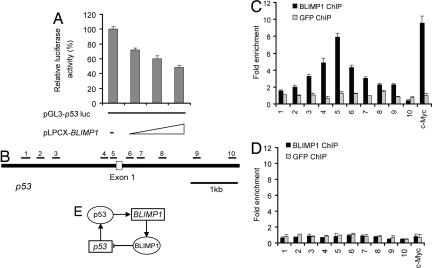
Fig. 5.
BLIMP1 directly suppresses p53 transcription by binding to its promoter. (A) Overexpression of BLIMP1 suppressed p53 promoter activity. Vectors expressing BLIMP1 (pLPCX-BLIMP1) and pGL3-p53luc were transiently cotransfected into HCT116 cells, and luciferase activity was measured 30 h after transfection. (B) Mapping of BLIMP1 binding across the p53 promoter using 10 primer sets. The locations of the amplified products of the primer sets used to detect the ChIP-enriched DNA fragments are shown within the context of the genomic structure of human p53. Amplicons are numbered in order relative to their sites along the gene. ChIP assays were performed by using HCT116 cells transiently transfected with pLPCX-BLIMP1 (C) or vector pLPCX alone (D). Real-time PCR was performed with immunoprecipitated chromatin fragments obtained by using anti-BLIMP1 antibody or an irrelevant antibody (anti-GFP) as control. A known BLIMP1 binding site in the promoter region of c-Myc gene was amplified as a positive control for the ChIP assays. (E) A model for the negative feedback loop between p53 and BLIMP1. The loop creates a circuit composed of BLIMP1, whose mRNA synthesis is influenced by the activation of p53, and this in turn results in the alteration of p53 activity in cells.