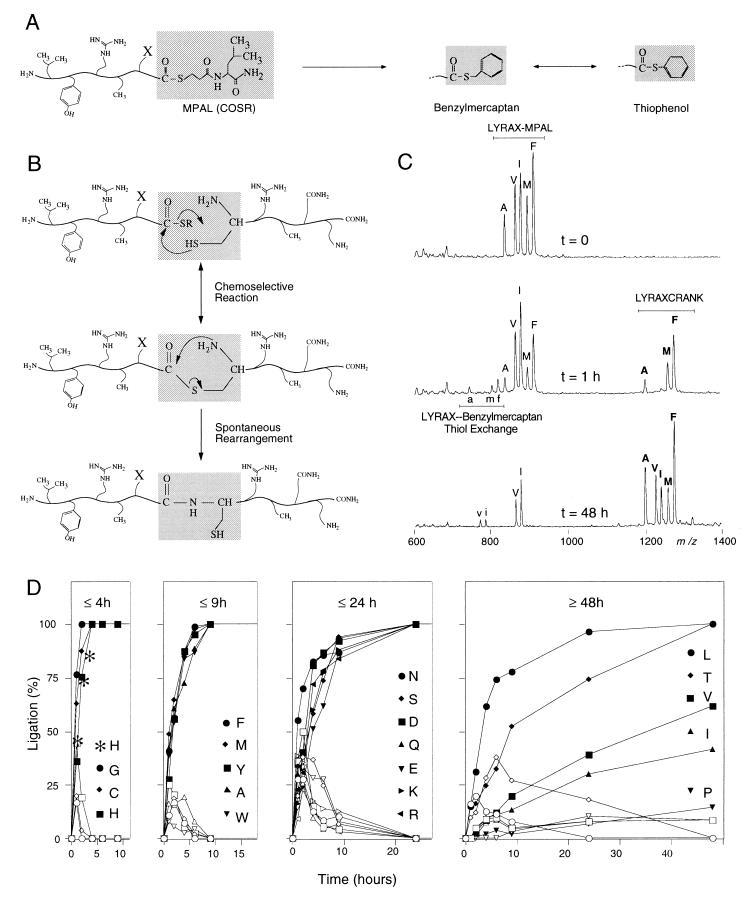
Figure 1.
Parallel native chemical ligation model study of LYRAX-to-CRANK peptide ligations, with X representing all 20 natural amino acids. (A) Under experimental conditions during native chemical ligation, LYRAX–MPAL-activated thioester peptides undergo thioester exchange reactions with benzylmercaptan and thiophenol. (B) Native chemical ligation. COSR of LYRAX–MPAL undergoes nucleophilic attack by the side chain of the N-terminal cysteine residue of CRANK, after which a rapid intramolecular rearrangement produces a native peptide bond at the site of ligation. (C) Simultaneous MALDI-MS readout of combinatorial ligations of crude LYRAX–MPAL-to-CRANK ligations featuring A, V, I, M, and F as C-terminal amino acid-activated thioester residues. (D) Determination of ligation product (filled symbols) and benzylmercaptan–thioester exchange intermediates (open symbols) as a function of time for all 20 LYRAX–MPAL C-terminal activated thioesters. C-terminal amino acids are divided into four groups, in which ligations were completed within 4, 9, or 24 hr or in 48 hr or more, respectively. Left, (t ≤ 4 hr), ∗ indicates the observed LYRAH–CRANK model-peptide ligation rate when monitored by using HPLC analysis.