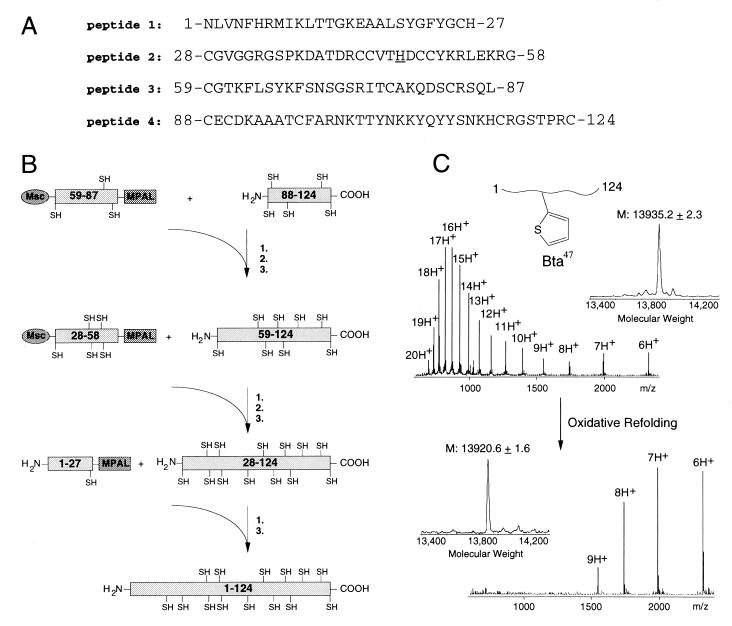
Figure 2.
Protein synthesis by multistep ligation: hsPLAA2. (A) Sequence of the four peptides comprising the 124-aa polypeptide chain of hsPLA2. Ligation sites include His(Dnp)–Cys, Gly–Cys, and Leu–Cys. In a parallel synthesis, the underlined His-47 active-site residue was replaced by the isosteric Bta to obtain a chemical hsPLA2 variant. (B) Synthetic scheme leading to the 124-aa hsPLA2 polypeptide chain. Typically, unprotected purified peptides were dissolved at 10 mg/ml in 0.1 M phosphate buffer containing 6 M guanidine and 4% benzylmercaptan and thiophenol reaching pH ≈ 7 (1). To avoid polymerization reactions, N-terminal cysteine residues of the activated thioester peptides were protected with Msc groups. After ligation, a 5-min treatment at pH 13 removed N-terminal Msc (2). HPLC yielded the purified ligation product. (3). (C) Electrospray ionization-MS of the reduced polypeptide chain of hsPLA2–Bta-47 (Upper) and the oxidized refolded enzyme variant (Lower). Mass reconstructions from the m/z ratios show a mass decrease from 13,935 Da to 13,921 Da representing the loss of 14 protons in the formation of seven internal disulfide bonds.