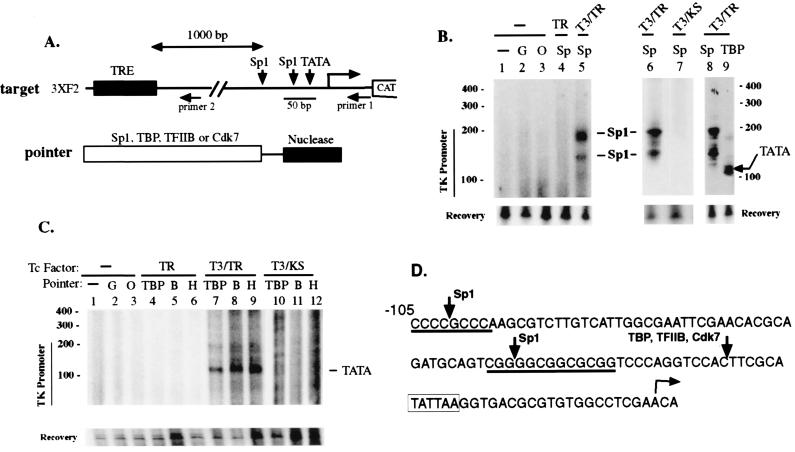
Figure 1.
Using PIN*POINT to study in vivo transcription factor recruitment during transcriptional silencing and activation of the TRE-regulated reporter gene. (A) Diagram of the target plasmid and pointers. The target DNA, 3XF2 TRE, contains three copies of the high-affinity TRE (30 bp) (ttatTGACCCCAgcTGAGGTCAagttacga, capital letters indicate inverted TREs) from the chicken lysozyme silencer F2 (31) inserted 1-kb 5′ upstream of the herpes simplex virus TK −105/+55 promoter. The TK promoter contains two Sp1 sites at −105/−95 and −56/−45 and the TATA box at −26/−21 position. Horizontal arrows mark the positions of the 3′ antisense primers (primer 1 and primer 2) used for LM-PCR in this study. Primer 1 was derived from the +26/+55 region of the TK promoter and was used to detect cleavage within the TK promoter; primer 2 was derived from a region 51–80 bp downstream from the 3′ end of the 3XF2 TRE and was used to detect cleavage within the TRE region. The pointers were composed of the 25-kDa nuclease domain of FokI restriction endonuclease fused to the carboxyl terminus of Sp1, TBP, TFIIB, or Cdk7 through a flexible glycine linker and were expressed by cotransfecting with the target plasmid. (B) Analysis of recruitment of Sp1 pointer to the TK promoter during the TR-mediated activation and silencing. HeLa cells were cotransfected with target plasmid 3XF2, a TR expression vector (wild type, TR; mutant KS, KS) and one of the pointer expression vectors (G, GAL4 DNA-binding domain; O, Oct-1; Sp, Sp1). Treatment of transfected cells with T3 is indicated. Approximately 24 hr after transfection, the target plasmid was harvested and LM-PCR was performed with primers 1 and MK21 (from the linker). The amplified fragment was detected with Southern blotting followed by hybridization with a radioactively labeled internal probe MK24. The amount of target plasmid was similar in each sample (recovery). The positions of the Sp1 binding sites and the TATA box are indicated. (C) Recruitment of basal transcription factors to the TK promoter during the TR-mediated activation and silencing. Experiments were performed as described for B except that pointers for TBP, TFIIB (B), or TFIIH (H) were used. (D) The cleavage sites for the Sp1 and basal transcription factor pointers as determined against a sequence ladder. Primer extension was performed on the LM-PCR products with radioactively labeled primer 1 and electrophoresed next to a DNA sequence ladder as described previously (29). The cleavage site by each pointer was deduced by subtracting the length of the ligated 29-bp linker (MK21/MK22). By comparing the intensities of the LM-PCR band generated from pointer cleavage with the LM-PCR band generated from the recovered DNA that has been digested with EcoRI, we estimate that approximately 3–4% of the target plasmid was cleaved by the pointers (data not shown).