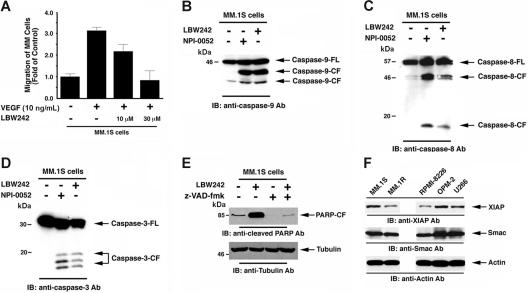
Figure 5.
LBW242-induced signal transduction in MM cells. (A) LBW242 inhibits VEGF-induced migration of MM cells. Growth factor–deprived MM.1S cells were either pretreated with indicated concentrations of LBW242 or left untreated. Cells were then plated on a fibronectin-coated polycarbonate membrane in a modified Boyden chamber and exposed for 4 hours to VEGF (5 ng/mL) in the lower chamber. Cells on the lower part of the membrane were then counted with a Coulter counter ZBII (mean ± SD; n = 2). (B-D) LBW242 induces both extrinsic and intrinsic apoptotic signaling MM.1S cells were treated with LBW242 (10 μM) for 48 hours or NPI-0052 (7 nM) for 24 hours and harvested; the total protein extracts were subjected to immunoblot analysis with anti–caspase-9 (B), caspase-8 (C), or caspase-3 (D) Abs. Lysates from NPI-0052–treated MM.1S MM cells served a positive control. (E) MM.1S cells were treated with LBW242 in the presence or absence of z-VAD-fmk for 24 hours and harvested; total protein extracts were subjected to immunoblot analysis with anticleaved PARP Abs. (F) Total protein lysates from MM.1S, MM.1R, RPMI-8226, OPM2, and U266 MM cells were subjected to immunoblot analysis with anti-XIAP (top panel), anti-Smac (middle panel), or antiactin (bottom panel) Abs.