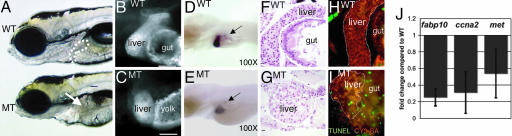
Fig. 1.
hi272 mutant embryos have a small-for-size liver on day 5. (A) WT and MT liver day 5 embryos from hi272. The liver in phenotypically WT embryo is visible anterior to the intestinal bulb (white outline); the expected position of the liver in the MT is indicated by an arrow. (B and C) CY3-SA labeling of day 5 WT (B) and MT embryos (C). The gut in the mutant is malformed and does not stain with CY3-SA, and the yolk consumption is incomplete in the mutant by day 5, and thus is labeled with CY3-SA. (Scale bar: 50 μm.) (D and E) In situ hybridization with fabp10 and insulin probes on WT (D) and MT (E) embryos. Arrows point to pancreatic islets, labeled with insulin. (F and G) H&E-; stained sagittal sections of livers from WT(F) and MT (G) embryos. Images were taken through the widest section of the left liver lobe. (Scale bar: 10 μm.) (H and I) Apoptotic cells (green) are not seen in the CY3-SA labeled liver (white outline) and gut of WT (H) but are plentiful in MT (I) embryos. (J) Q-PCR on cDNA prepared from day 5 WT and MT embryos from hi272. Expression levels relative to tbp were calculated and shown as fold change compared with phenotypically WT siblings. The experiment was run in triplicate; bars indicate SD.