Figure 2. .
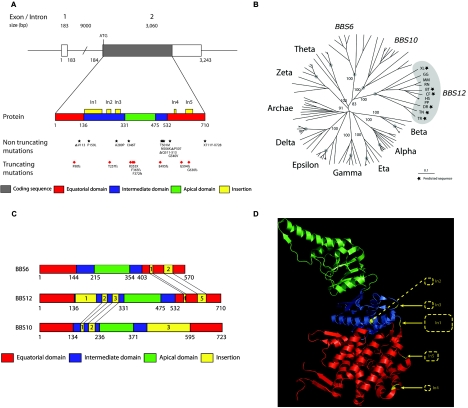
Schematic of the BBS12 locus and the position and/or nature of mutations. A, BBS12 genomic locus (top), corresponding to FLJ35630 (NCBI [RefSeq] accession number NM_152618). FLJ35630 encodes a predicted protein of 710 aa (UniProt accession number Q6ZW61_HUMAN). The bottom section is a schematic of the protein with the recognized domains in different colors (see key). The insertions in the intermediate and equatorial domains are shown as yellow boxes above the protein. All reported mutant alleles are shown underneath the protein. B, Phylogenetic tree of the BBS family. The tree contains BBS12, BBS10, and BBS6 sequences and representative sequences from all group II chaperonins. BBS12 genes are highlighted with organism abbreviations, and predicted sequences are marked with a black star. XL = X. laevis; GG = G. gallus; MM = M. musculus; RN = R. norvegicus; BT = B. taurus; CF = C. familiaris; HS = H. sapiens; PP = Pongo pygmaeus; DR = D. rerio; TN = T. nigroviridis; TR = T. rubripes. The roots of vertebrate branches are highlighted with gray dots. Bootstrap values are provided for significant nodes when they are >80%. C, Comparison of BBS chaperonin-like domain organization. BBS12, BBS10, and BBS6 are represented with the typical chaperonin group II organization in three domains (equatorial, intermediate, and apical). Specific insertions to the typical chaperonin group II are drawn in yellow and are numbered in order of appearance from N-ter to C-ter part. Points of insertions that appear common to BBS12 and BBS6 and to BBS12 and BBS10 are highlighted with black lines. D, Ribbon drawing of group II chaperonin α subunit (Protein Data Bank 1q2v). Domains are colored according to figure 3A. BBS12 insertions (In1-In5) relative to all group II chaperonin sequences are represented as yellow dashed rectangles.