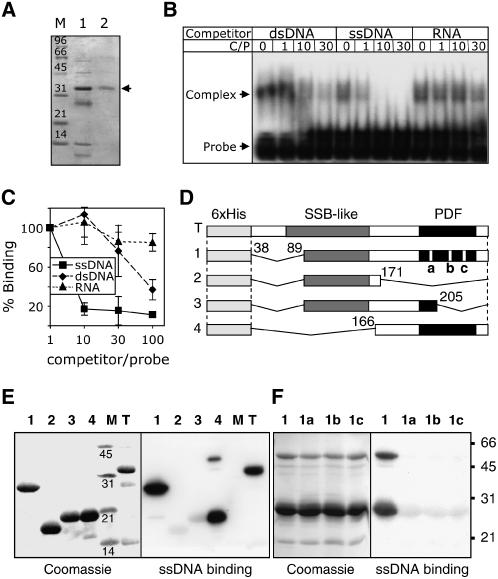
Figure 3.
ssDNA Binding Activity of At OSB1.
(A) Nickel-nitrilotriacetic acid agarose affinity chromatography purification of soluble At OSB1 expressed in E. coli. Lane 1, proteins eluting with 50 mM imidazole; lane 2, purified protein eluting with 150 mM imidazole.
(B) Electrophoretic mobility shift assay of nucleic acid binding. At OSB1 and 32P-labeled ssDNA probe were incubated with increasing quantities of cold competitor before electrophoresis. dsDNA, ssDNA, and RNA competitors were of the same size and sequence as the probe. The molar ratio of competitor to probe (C/P) is given. At OSB1/ssDNA complexes are shown by arrowheads.
(C) At OSB1 purified under denaturing conditions was tested on protein/DNA gel blots for binding to labeled ssDNA in the presence of increasing concentrations of cold competitor (ssDNA, dsDNA, or RNA). Results were quantified using a phosphor imager. Error bars indicate the sd of three independent experiments.
(D) Structure of At OSB1 mutants expressed in E. coli. SSB-like, PDF, and deleted regions are indicated. a, b, and c refer to the double substitution mutations described for Figure 2B.
(E) Analysis of ssDNA binding by At OSB1 mutant proteins. Expressed proteins described for (D) were fractionated by SDS-PAGE, transferred to polyvinylidene difluoride membranes, and probed with labeled ssDNA.
(F) Same as (E) using construct 1 with mutation a, b, or c.