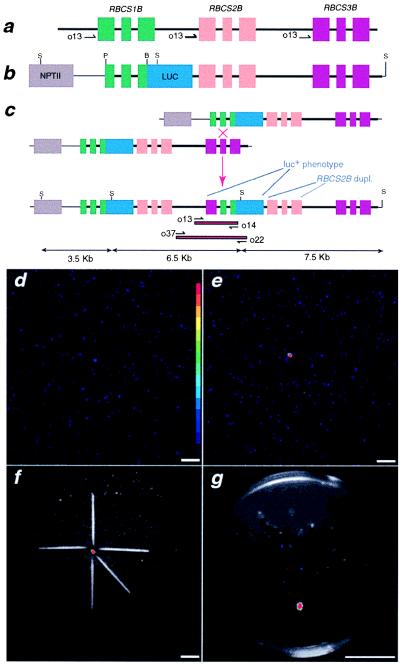
Figure 1.
Genetic constructs and isolation of luc+ seedlings. (a) The A. thaliana RBCSB locus. The black line indicates noncoding genomic DNA. Exons shown in color: RBCS1B (green), RBCS2B (orange), and RBCS3B (red). Sizes of introns and exons are not to scale but rather represent genetic organization. Restriction enzymes: P, PflMI; B, BsmI; and S, SphI. Labeled black half-arrows indicate respective oligonucleotide primer-binding sites. (b) Synthetic RBCSB gene cluster construct. NPTII gene is shown in gray. ΔRBCS1B∷LUC fusion consisted of RBCS1B sequences from the PflMI in exon I to the BsmI site in exon III; firefly luciferase-NOS 3′ terminator (blue) was cloned in-frame 3′ to RBCS1B exon III. RBCS2B-RBCS3B sequences were positioned 3′ to the ΔRBCS1B∷LUC fusion. (c) An unequal crossover event between sister chromatids containing the synthetic RBCSB gene cluster. Red boxes with black borders define the region of gDNA amplified by PCR with the respective oligonucleotide primers. (d) Ten-minute photon-counting image of empty imaging chamber. (Inset) Pseudocolor step gradient depicting low photon density (light blue) to high photon density (red). [Bar = 4 cm (d–g).] (e) Ten-minute photon-counting image of a tray containing approximately 7,500 F2 seedlings with 1 luc+ seedling (red spot). (f) Image from e superimposed on reflected green-light image of the same tray on which toothpicks were placed to approximate the location of the luc+ seedling. (g) Twenty-five seedlings transferred from the tray in f onto a 0.8% water agar Petri plate. A photon-counting image superimposed on a reflected green-light image allowed the unambiguous identification of a single luc+ seedling on the Petri plate.