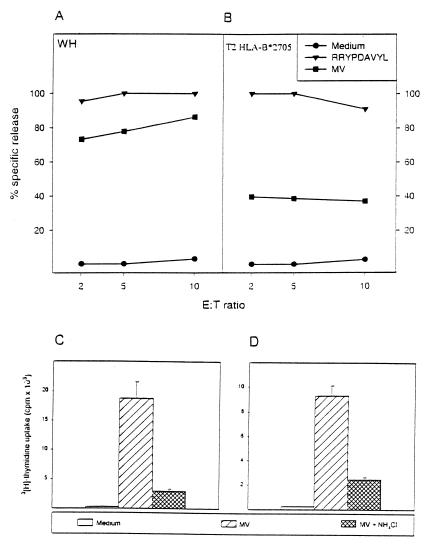
Figure 1.
TAP-independent and NH4Cl-sensitive presentation of the MV-F protein to MHC class I-restricted T cell clones. Autologous EBV- transformed B lymphoblastoid cell lines (EBV B-LCL) WH (A) and the T2 HLA-B*2705 transfectant (B) were infected either with MV at a multiplicity of infection of 3.0, sham-infected, or pulsed with 1 μM peptide (RRYPDAVYL) for 24 h, as indicated. Cells were used as targets in a 4-h 51Cr release assay with the MV-F-specific CTL clone WH-F40 at effector-to-target (E:T) cell ratios of 2, 5, and 10. Results are expressed as the mean percentages of specific target cell lysis of triplicate cultures. Both peptide pulsed targets were killed with equal efficiency. TAP-deficient T2 HLA-B*2705 transfectant was efficiently lysed. To determine whether class I-restricted presentation is affected by lysosomotropic agents, EBV B-LCL JP (C) and WH (D) were infected with MV in the presence or absence of 20 mM NH4Cl. Fixed cells were used as stimulator cells for JP III.8 (C) and WH-F40 T cell clones (D) in a proliferative T cell assay. cpm ± SD of triplicate cultures are shown. Treatment of stimulator cells during MV infection with NH4Cl inhibits their capacity to present MV-F protein-derived peptide in a MHC class I-restricted fashion.