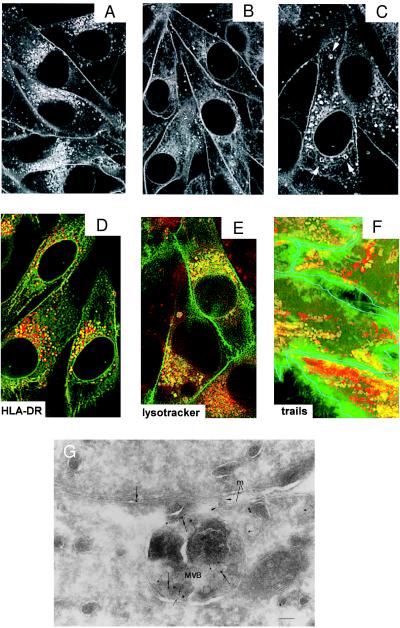
Figure 3.
HLA-A2-GFP-containing endosomal vesicles have similar features as MIICs. Confocal analysis of the intracellular distribution of HLA-A2-GFP in living Mel JuSo HLA-A2-GFP stimulated for 48 h with 200 units/ml of IFN-γ and cultured at 37°C (A) without any further treatment. Fluorescence is observed at the cell surface and in perinuclear and peripheral vesicles. (B) Transfectants after additional treatment with 10 μg/ml BFA for 4 h resulting in a strong decrease of the amount of fluorescent perinuclear vesicles and (C) after additional treatment with 100 μM chloroquine for 30 min. Chloroquine causes swelling of a fraction of the HLA-A2-GFP-containing vesicles (indicated by arrows). (D) Merged image of double labeling of fixed Mel JuSo HLA-A2-GFP (green) stained with anti-HLA-DR antibodies visualized with Texas Red-conjugated secondary antibodies. Colocalization is seen in yellow because of the combination of the green and red signal showing that a fraction of the HLA-A2-GFP-containing vesicles is positive for MHC class II molecules. (E) Merged image of double labeling of living Mel JuSo HLA-A2-GFP cells incubated with LysoTracker Red to label acidic compartments showing that a fraction of the HLA-A2-GFP-containing vesicles is acidic. (F) Trail analysis of moving vesicles in living Mel JuSo HLA-A2-GFP cells incubated with LysoTracker Red. Images of the moving vesicles were made every sec for 1 min and all 60 images were superimposed. Green trails are created by vesicles that contain only HLA-A2-GFP, yellow trails are created by vesicles that contain HLA-A2-GFP and LysoTracker Red, and red trails are created by vesicles that contain only LysoTracker Red. For clarity, the cell surface of the different cells is outlined in blue. A fraction of HLA-A2-GFP vesicles are acidic and move as MIIC vesicles. (G) Fusion of a class I-containing multivesicular body (MVB) with the plasma membrane. Mel JuSo HLA-A2-GFP stimulated for 48 h with 200 units/ml of IFN-γ were fixed, and cryosections were labeled with anti-CD63 (5 nm gold; small arrows) and anti-MHC class I heavy chain (10 nm gold; large arrows) antibodies. A MVB trapped in the process of fusion with the plasma membrane (m) and containing both class I and CD63 is shown. Note the continuity of the limiting membrane of the MVB with the plasma membrane (arrowheads) and that the lumen is open to the intercellular space between two cells. (Bar: 100 nm.)